what is poly aluminium chloride
What is Poly Aluminium Chloride?
Poly Aluminium Chloride, commonly abbreviated as PAC, is an inorganic polymer that plays a crucial role in various applications, particularly in water treatment processes. Its chemical composition consists of aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) and hydrochloric acid (HCl), which together form a coagulant that is effective in clarifying and purifying water. PAC is recognized for its ability to remove impurities, turbidity, and dissolved organic matter from the water, making it an essential component in both municipal and industrial water treatment facilities.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Poly Aluminium Chloride is a polymeric compound, which means it is formed through the polymerization of monomeric units. The typical chemical formula can vary, but it generally contains multiple aluminum ions linked together. The polymeric structure enhances the coagulant's efficiency in particle aggregation due to the increased surface area. This characteristic allows PAC to bind with suspended particles in water more effectively than traditional coagulants like aluminum sulfate (alum).
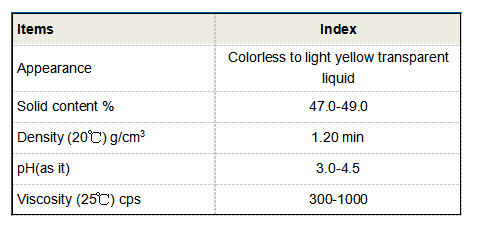
PAC is available in various forms, including liquid and powder, and it can be produced with differing molecular weights and basicities, allowing for customization based on specific water treatment needs. The basicity of PAC indicates the ratio of hydroxyl ions to aluminum ions in the product, influencing its effectiveness in different water conditions.
Applications in Water Treatment
One of the primary applications of Poly Aluminium Chloride is in water purification and municipal wastewater treatment. When added to water, PAC forms a gelatinous precipitate that traps impurities, such as bacteria, dirt, and other suspended solids. This process, known as coagulation, facilitates the removal of these unwanted materials through sedimentation, filtration, or flotation processes.
PAC has several advantages over traditional coagulants. Its higher efficiency allows for lower dosages, which can lead to reduced costs in both material and operational aspects of water treatment. Moreover, PAC is capable of operating effectively across a broader pH range, making it suitable for diverse water sources, including surface water, groundwater, and industrial waste streams.
In addition to municipal applications, PAC is also employed in various industries, such as paper manufacturing, textiles, and food processing. In these sectors, it is used to clarify process water, enhance product quality, and manage waste effluents.
what is poly aluminium chloride
Benefits of Using PAC
The use of Poly Aluminium Chloride offers several benefits
1. Effectiveness PAC is known for its superior coagulating properties, which significantly improve the clarity of treated water compared to traditional methods.
2. Cost-Effectiveness Due to its efficiency, PAC can reduce the overall treatment costs by lowering the quantities needed for effective coagulation.
3. Versatility Its ability to function at various pH levels allows PAC to treat a wide range of water types, enabling its use in different settings from drinking water treatment to industrial processes.
4. Reduced Sludge Production Compared to alum, PAC generates less sludge during the coagulation process, which simplifies disposal and management.
5. Environmental Friendliness PAC is considered to have a lower environmental impact due to its reduced chemical footprint and lower levels of undesirable residuals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Poly Aluminium Chloride is a vital coagulant in the field of water treatment, recognized for its effectiveness, versatility, and cost-efficiency. Its ability to remove impurities from water makes it an invaluable resource for ensuring safe and clean water supplies in both municipal and industrial applications. As global water quality concerns continue to rise, the role of PAC and similar chemical treatments is set to become increasingly significant in the quest for sustainable and efficient water management solutions.
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride: High-Purity DisinfectantNewsAug.30,2025
-
2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid: Scale & CorrosionNewsAug.29,2025
-
Premium Isothiazolinones | Broad-Spectrum Biocidal SolutionsNewsAug.28,2025
-
LK-319 Special Scale And Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Plants: Advanced Solutions for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: Essential Chemical Solutions for Purification ProcessesNewsAug.22,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: Versatile Microbial Control Agents for Industrial and Consumer ApplicationsNewsAug.22,2025





