Zinc HEDP Applications and Benefits in Industrial Processes
Exploring the Benefits and Applications of Zn-EDP (Zinc EDP)
Zinc EDP, primarily known as Zn-EDP, stands for Zinc Ethylenediamine Tetra (methylene phosphonic) Acid. It is a compound that has garnered significant attention due to its unique properties and wide range of applications, particularly in the fields of agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and industrial processes.
Exploring the Benefits and Applications of Zn-EDP (Zinc EDP)
In addition to its agricultural applications, Zn-EDP is also utilized in the pharmaceutical industry. Research has indicated that zinc is vital for maintaining a healthy immune system and plays a role in wound healing and DNA synthesis. Zn-EDP is often found in various formulations aimed at improving health outcomes. Its ability to stabilize zinc ions makes it a preferred choice in supplement formulations, ensuring that users receive the appropriate dosage of zinc without the common side effects associated with other forms of zinc.
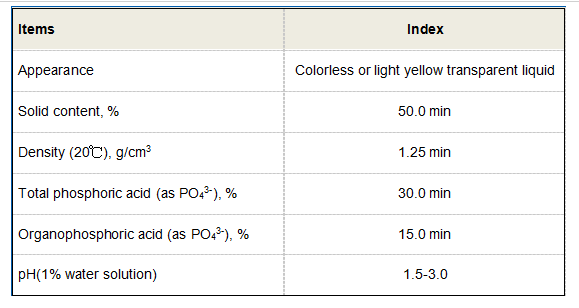
'zn hedp 锌hedp'
Another significant use of Zn-EDP lies within industrial applications, particularly in water treatment and corrosion inhibition. Water quality management is critical in ensuring the safety and health of communities. Zn-EDP acts as an effective chelating agent, binding with metals and preventing their precipitation and subsequent accumulation in wastewater systems. It also imparts corrosion resistance to various materials, extending the lifespan of industrial equipment and reducing maintenance costs.
Moreover, Zn-EDP's versatility allows it to be used in other domains, such as the production of fertilizers and soil conditioners. By incorporating Zn-EDP into their formulations, manufacturers can create more effective products that enhance soil health and improve crop yields. This is particularly important in regions with zinc-deficient soils, where the addition of Zn-EDP can significantly boost agricultural productivity.
Another exciting area of research is the role of zinc in nanotechnology. Zn-EDP is being explored for its potential in the development of nanomaterials, which can have applications across various sectors, including electronics, energy storage, and drug delivery systems. The unique properties of Zn-EDP can contribute to the creation of innovative materials with enhanced functionalities.
In conclusion, Zn-EDP is a multi-faceted compound with promising applications across agriculture, pharmaceuticals, industrial processes, and beyond. Its ability to provide essential nutrients, enhance the performance of products, and contribute to environmental sustainability positions it as a vital component in contemporary science and industry. As research continues to uncover the potential of this compound, we can expect to see even broader applications and enhanced formulation strategies that utilize Zn-EDP for a sustainable future. Through informed use, Zn-EDP may very well play a key role in addressing some of the pressing challenges facing our planet today.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





