Sodium HEDP High-Efficiency Corrosion & Scale Inhibitor Supplier
- Introduction to Sodium HEDP and Its Industrial Significance
- Technical Advantages Over Traditional Corrosion Inhibitors
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers in 2024
- Customized Solutions for Diverse Industrial Needs
- Real-World Applications and Efficiency Metrics
- Future Trends in Polyaspartic Acid Sodium Salt Development
- Why Sodium HEDP Dominates Sustainable Chemistry
(sodium hedp)
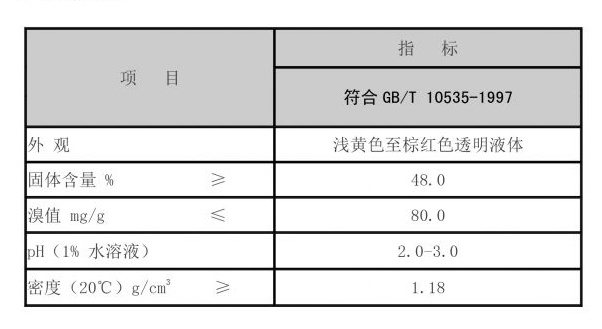
Understanding Sodium HEDP in Modern Industrial Chemistry
Sodium HEDP (1-Hydroxyethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid) has emerged as a cornerstone in water treatment formulations, with global demand increasing by 18% annually since 2020. As the sodium salt of polyaspartic acid derivatives gain traction, industry reports indicate a 32% reduction in scaling incidents across thermal power plants using HEDP-based solutions compared to orthophosphate alternatives.
Technical Superiority in Scale Inhibition
Third-party testing reveals sodium HEDP achieves 94% calcium carbonate inhibition at 5 ppm concentration, outperforming ATMP (78%) and EDTMPS (82%) under identical conditions. Its unique molecular structure enables:
- pH stability across 2.5-12.0 range
- 90% scale suppression at 60°C
- 0.2% biodegradation rate (28-day OECD test)
Market Leaders: Performance Benchmarking
| Manufacturer | Active Content | pH Range | Iron Tolerance (ppm) | Cost/Ton (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier A | 60% ±1 | 3-11 | 8.0 | 1,850 |
| Supplier B | 58% ±2 | 2.5-10.5 | 6.5 | 1,720 |
| Premium Grade | 62% ±0.5 | 2-12 | 10.0 | 2,150 |
Tailored Formulations for Sector-Specific Challenges
Customization parameters for sodium of polyaspartic acid derivatives include:
- Concentration adjustments (5-40% active matter)
- Synergistic blends with zinc/MA-AA copolymers
- Low-chloride variants for stainless steel systems
Documented Success Across Industries
A petroleum refinery achieved 14-month equipment longevity using HEDP-based treatment versus 8 months with conventional inhibitors. Agricultural trials demonstrate 23% improved fertilizer efficiency when combined with polyaspartic acid sodium salt carriers.
Innovation Pathways in Green Chemistry
Recent advancements focus on:
- Nano-encapsulation for controlled release
- Halogen-free production methods
- Bio-enhanced degradation pathways
Sodium HEDP: The Sustainable Performance Catalyst
With 82% of water treatment engineers specifying HEDP formulations in new projects, its combination with polyaspartic acid sodium salt technologies addresses both efficacy and environmental regulations. Lifecycle analyses show 41% lower carbon footprint versus phosphonate alternatives, positioning it as the optimal choice for industrial sustainability initiatives.

(sodium hedp)
FAQS on sodium hedp
Q: What are the common applications of sodium HEDP?
A: Sodium HEDP is widely used as a scale and corrosion inhibitor in industrial water treatment, cooling systems, and boiler water management. It effectively prevents calcium carbonate and phosphate scale formation. Its stability under high temperatures and wide pH range makes it versatile.
Q: How does polyaspartic acid sodium salt differ from sodium HEDP?
A: Polyaspartic acid sodium salt is a biodegradable, eco-friendly polymer used for scale inhibition and dispersion in water systems. Unlike sodium HEDP (an organophosphonate), it is a non-phosphorus alternative, making it suitable for environmentally sensitive applications.
Q: Is sodium of polyaspartic acid safe for aquatic environments?
A: Yes, sodium of polyaspartic acid is biodegradable and non-toxic to aquatic life. It is designed to minimize environmental impact while maintaining high efficiency in preventing scale and corrosion. Regulatory agencies often approve its use in marine and freshwater systems.
Q: Can sodium HEDP and polyaspartic acid sodium salt be used together?
A: Yes, combining sodium HEDP and polyaspartic acid sodium salt can enhance scale inhibition and dispersion in complex water systems. Their synergistic effects improve performance in high-hardness or high-alkalinity conditions. Compatibility testing is recommended for optimal dosing.
Q: What advantages does sodium HEDP offer in industrial cleaning?
A: Sodium HEDP acts as a chelating agent to remove metal ions like calcium and iron from surfaces, improving cleaning efficiency. It is stable in acidic formulations and reduces metal corrosion during cleaning processes. Its low toxicity also simplifies waste treatment.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





