pbtc tricarboxylic acid
Understanding PBTC and Its Role in Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that plays a crucial role in cellular respiration. It is vital for the conversion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Among the various compounds involved in this cycle, phosphonobutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid (PBTC) has garnered attention due to its unique properties and its potential applications in biochemistry and environmental science.
PBTC is a compound containing phosphonic acid and carboxylic acid functional groups, which makes it an excellent candidate for various biochemical applications. The presence of these functional groups allows PBTC to interact effectively with metal ions and other biomolecules, making it significant in chelation and binding processes.
The Role of PBTC in the TCA Cycle
Within the TCA cycle, two main functions of PBTC are highlighted its involvement in enzyme regulation and its potential role as a metabolic intermediate. Enzymes such as citrate synthase and aconitase are essential participants in the TCA cycle, facilitating the transformation of substrates into products. Research indicates that compounds like PBTC might modulate the activity of these enzymes through competitive inhibition or by altering their conformational properties.
Furthermore, the structural similarity of PBTC to intermediates in the TCA cycle, such as citrate and isocitrate, suggests that it could act as a metabolic intermediary. This possibility opens new avenues for research into how PBTC might be utilized to enhance energy production or to influence metabolic pathways in various organisms.
Applications and Implications
The potential applications of PBTC extend beyond its involvement in the TCA cycle. Its unique chemical structure makes it valuable in various fields, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. In agriculture, PBTC can act as a chelating agent, improving the availability of essential micronutrients to plants. It can help in preventing the precipitation of metal ions in soils, thereby enhancing nutrient uptake.
pbtc tricarboxylic acid
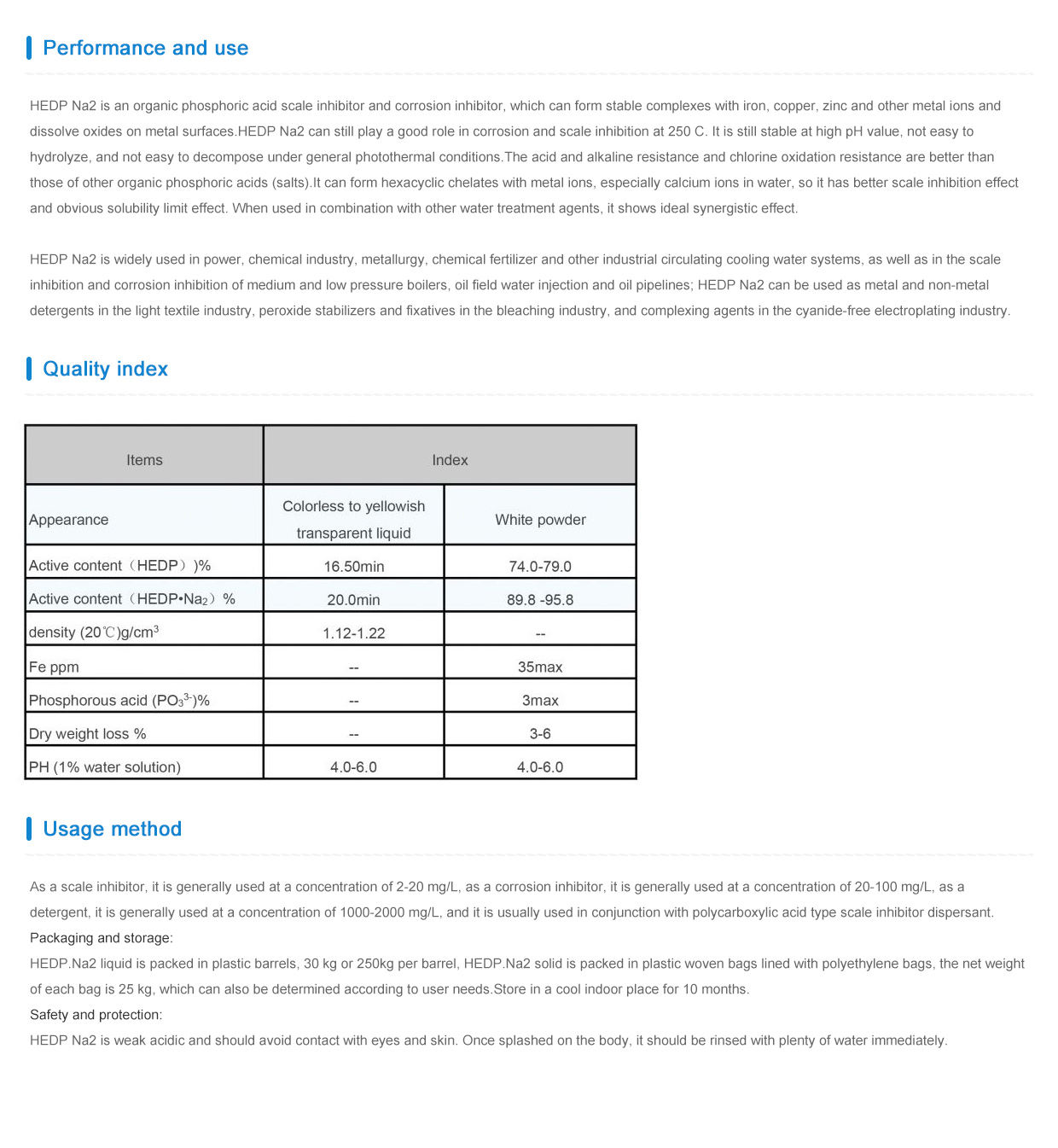
In pharmaceuticals, understanding how PBTC interacts with biological systems can lead to the development of new drugs that target metabolic pathways more effectively. For instance, drugs that incorporate PBTC or its analogs might be designed to enhance mitochondrial function or to regulate metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and obesity.
Environmental Impact
Besides its application in biochemistry, PBTC’s relevance extends to environmental science. By functioning as a chelator, it can play a role in bioremediation efforts, where it helps in immobilizing heavy metals and preventing their bioavailability in contaminated sites. This property is particularly relevant in addressing issues related to soil and water pollution, thereby promoting sustainability and environmental health.
Research Directions
Despite the promising applications of PBTC, further research is necessary to fully understand its mechanisms, interactions, and efficacy in various contexts. Studies focusing on the biochemical pathways influenced by PBTC, as well as its interactions with different metal ions and biomolecules, will be pivotal in unlocking its potential. Moreover, the exploration of synthetic routes to more potent analogs of PBTC may lead to the discovery of new compounds with enhanced properties.
Conclusion
In summary, phosphonobutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid (PBTC) is a compound of significant interest within the realm of biochemistry, particularly concerning its role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Its unique structural characteristics present it as a versatile agent with potential applications in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and environmental science. However, extensive research is essential to harness its full potential and to understand the complexities of its interactions within biological systems and ecosystems. Exploring these avenues could lead to breakthroughs in metabolic regulation, environmental sustainability, and agricultural productivity, highlighting the importance of PBTC in both science and industry.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





