Structure and Properties of Polyaspartic Acid and Its Derivatives in Biochemical Applications
The Structure and Applications of Polyaspartic Acid
Polyaspartic acid is a synthetic polymer derived from aspartic acid, an amino acid that plays a vital role in various biological processes. The structure of polyaspartic acid consists of repeating units of aspartic acid residues linked together by peptide bonds, resulting in a polymer chain that exhibits unique physical and chemical properties. This article explores the structure, characteristics, and diverse applications of polyaspartic acid.
Structural Overview
Polyaspartic acid is categorized as a polyamino acid due to its composition. The basic repeating unit in polyaspartic acid contains a carboxyl (-COOH) group and an amino (-NH₂) group, which enable it to engage in a variety of interactions with other molecules. The polymer can exist in different forms depending on its molecular weight and degree of polymerization. Typically, it appears as a white powder and is soluble in water, which facilitates its use in various aqueous solutions.
The primary structure of polyaspartic acid includes a backbone of carbon atoms with side chains that contribute to its hydrophilicity. The presence of multiple carboxylic acid groups along the polymer chain endows polyaspartic acid with a high degree of ionization, which enhances its chemical reactivity and allows it to form chelates with metal ions. The stereochemistry of aspartic acid also plays a critical role in dictating the polymer's secondary structure, which can include alpha-helices or beta-sheets depending on environmental conditions such as pH and temperature.
Unique Properties
Polyaspartic acid exhibits several distinctive properties that make it appealing for industrial applications. One of the most notable characteristics is its ability to form films and coatings that are not only durable but also resistant to degradation from environmental factors. Moreover, polyaspartic acid is biodegradable, which sets it apart from many synthetic polymers that pose significant environmental challenges.
Another critical property of polyaspartic acid is its compatibility with various formulations, including adhesives, sealants, and paints. It can significantly enhance the performance of these materials by improving their adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to chemical attacks. This versatility is primarily due to the polymer's functional groups that can interact with different substrates and act as cross-linking agents.
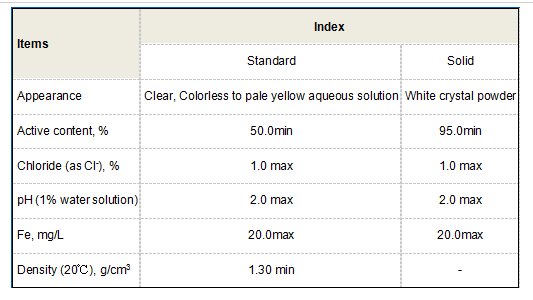
polyaspartic acid structure
Applications Across Industries
The unique characteristics of polyaspartic acid allow it to find applications across several industries
1. Coatings and Paints Polyaspartic acid is increasingly employed in the formulation of protective coatings for industrial applications. These coatings are known for their rapid curing times and superior hardness, making them ideal for harsh environments. They are commonly used on industrial floors, bridges, and automotive parts.
2. Biomedical Applications Due to its biocompatibility and low toxicity, polyaspartic acid is being investigated for use in biomedical applications. It can be used as a drug delivery vehicle, providing controlled release of therapeutic agents. Furthermore, it may serve as a scaffold material for tissue engineering, promoting cell adhesion and proliferation.
3. Agriculture In agricultural settings, polyaspartic acid acts as a biostimulant that enhances nutrient bioavailability and improves plant growth. Its ability to chelate metal ions enables it to solubilize micronutrients in the soil, making them more accessible to plants.
4. Personal Care Products The polymer's emulsifying and thickening properties make it suitable for formulation in personal care products, such as lotions and shampoos. Polyaspartic acid enhances product texture and stability while providing skin benefits.
Conclusion
Polyaspartic acid is a remarkable polymer with a unique structure that resembles its amino acid precursor, aspartic acid. Its exceptional properties enable diverse applications in coatings, biomedicine, agriculture, and personal care products, highlighting its potential as a sustainable alternative to conventional materials. As research continues to explore the capabilities of polyaspartic acid, it is likely that more innovative uses will emerge, further establishing its importance in various fields.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





