Understanding Coagulants and Flocculants in Water Treatment Processes
Understanding Coagulants and Flocculants Key Agents in Water Treatment
Water treatment processes are critical for ensuring safe, clean water for human consumption and for various industrial applications. Among the various processes involved in water treatment, the use of coagulants and flocculants plays a pivotal role. These two agents are essential for the clarification of water and the removal of suspended particles, pathogens, and contaminants. This article explores the nature, functions, applications, and differences between coagulants and flocculants.
What Are Coagulants?
Coagulants are chemicals that promote the agglomeration of fine particles in suspension, helping to form larger clusters known as flocs. Commonly used coagulants include aluminum sulfate (alum), ferric chloride, and polyelectrolytes. When added to water, these substances neutralize the charges on suspended particles, allowing them to stick together and settle out of the liquid.
The coagulation process typically involves the rapid mixing of the coagulant into the water to ensure uniform distribution. This is followed by a flocculation process that allows the small agglomerated particles to collide and form larger aggregates. The use of coagulants is crucial in various applications, including municipal water treatment plants, wastewater management, and industrial processes.
The Role of Flocculants
Flocculants, while similar to coagulants in function, have distinct characteristics and applications. Flocculants are typically high molecular weight substances that enhance the process of coagulation by promoting the formation of larger flocs from the smaller aggregates created during coagulation. Common flocculants include synthetic organic polymers such as polyacrylamides, as well as natural substances like starches or gums.
In contrast to coagulants, which typically cause rapid agglomeration, flocculants work by gently stirring and allowing larger particles to form. The addition of flocculants after coagulation helps to increase the size and density of the flocs, facilitating their removal through sedimentation or filtration. Flocculants are often used in specific applications such as sludge dewatering, clarification of potable water, and various industrial processes.
coagulant flocculant
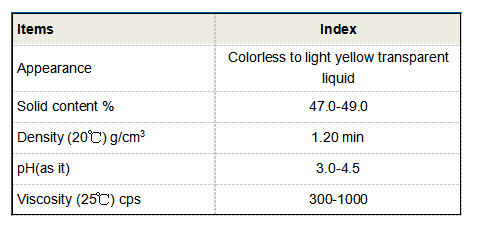
Differences Between Coagulants and Flocculants
While coagulants and flocculants are both used to clarify water, they serve different roles in the treatment process. The primary difference lies in their mechanism of action. Coagulants initiate the process by destabilizing the colloidal particles, while flocculants enhance the aggregation of these particles into larger clusters.
In terms of their chemical composition, coagulants are often inorganic salts or metal salts, whereas flocculants are typically long-chain polymers. This difference in molecular structure also impacts their handling and operational procedures in water treatment facilities. Proper dosage and application techniques must be carefully monitored due to the varying nature of these agents.
Applications in Water Treatment
The applications of coagulants and flocculants span a wide range of industries. In municipal water treatment, they are essential for ensuring compliance with health standards regarding turbidity and microbiological contaminants. For wastewater treatment facilities, these agents are vital for removing suspended solids and organic matter, contributing to the efficient processing of effluents before discharge.
In industrial settings, coagulants and flocculants play crucial roles in processes such as mining, paper manufacturing, and food processing, where clarity of water and removal of particulates are necessary. Furthermore, these agents are also employed in stormwater treatment systems to mitigate pollution runoff and enhance water quality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, coagulants and flocculants are integral to effective water treatment, working collaboratively to ensure the removal of impurities and clarity of water. Understanding their distinct roles, chemical properties, and applications enables water treatment professionals to optimize their use in various processes. As environmental regulations become more stringent and the demand for clean water increases globally, the significance of these agents in safeguarding public health and preserving water resources cannot be overstated. Advanced research continues to explore new coagulants and flocculants, aiming to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact, ensuring a sustainable future for water treatment practices.
-
LK-319 Special Scale And Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Plants: Advanced Solutions for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: Essential Chemical Solutions for Purification ProcessesNewsAug.22,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: Versatile Microbial Control Agents for Industrial and Consumer ApplicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor: Key Solutions for Water System Scale PreventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
Organophosphonates: Versatile Scale Inhibitors for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitor: Essential Chemical Solutions for Water System MaintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





