Synthesis and Applications of Non-Ionic Polyacrylamide in Various Industries
Non-Ionic Polyacrylamide Applications, Benefits, and Future Prospects
Non-ionic polyacrylamide (NIPAM) is a versatile polymer that has gained significant attention in various fields due to its unique properties. Unlike ionic polyacrylamides, which carry charged functional groups, non-ionic polyacrylamides do not possess any charge. This characteristic endows them with distinctive behavior in solution, making them ideal for specific applications across a range of industries.
Properties of Non-Ionic Polyacrylamide
The primary structure of non-ionic polyacrylamide is comprised of acrylamide monomers, which polymerize to form long chains. The absence of ionic groups means that NIPAM displays lower susceptibility to changes in environmental conditions such as pH and ionic strength. This stability is particularly beneficial in various applications where fluctuations in these conditions are common. Additionally, non-ionic polyacrylamide is known for its excellent water solubility and high molecular weight, which enhances its effectiveness as a thickening and gelling agent.
Applications in Various Industries
1. Water Treatment One of the most significant applications of non-ionic polyacrylamide is in water treatment processes. It is frequently used as a flocculant, where it aids in the aggregation of suspended particles, allowing for their efficient removal. By enhancing the settling rates of solids in water, NIPAM significantly improves the quality of treated water.
2. Agriculture In the agricultural sector, non-ionic polyacrylamide is utilized to improve soil structure and water retention. When applied to soil, it reduces erosion and compaction, thereby enhancing nutrient availability for plants. Additionally, its ability to form hydrogels can create a reservoir of moisture, beneficial in arid regions.
non ionic polyacrylamide
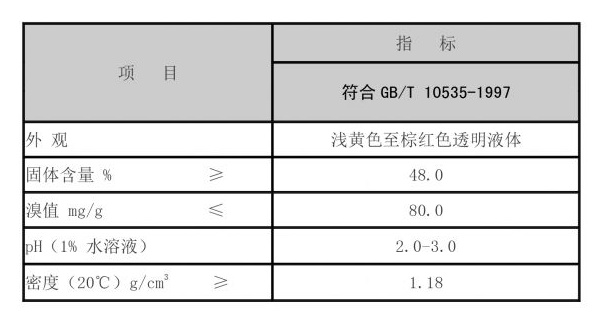
3. Biomedical Applications Non-ionic polyacrylamide has also found applications in the biomedical field. Its biocompatibility and non-toxicity make it suitable for drug delivery systems and tissue engineering scaffolds. Researchers are exploring NIPAM in the development of temperature-sensitive hydrogels that can release drugs in response to body temperature, optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
4. Paper and Textile Industries In papermaking and textile processing, non-ionic polyacrylamide is employed as a dispersant and sizing agent. Its film-forming ability enhances the properties of paper products and textile fabrics, imparting strength and water resistance.
Benefits of Using Non-Ionic Polyacrylamide
The advantages of using non-ionic polyacrylamide are manifold. Firstly, its non-ionic nature reduces the risk of adverse interactions with other chemicals, making it compatible with various formulations. Secondly, its ability to work effectively across diverse conditions provides significant flexibility in applications. Additionally, NIPAM is highly efficient at low concentrations, which further reduces overall costs and environmental impact.
Future Prospects
The future of non-ionic polyacrylamide appears promising as research continues to unveil new applications and optimization methods. Innovations in polymer chemistry could lead to the development of smart NIPAM-based materials that respond dynamically to environmental stimuli. Furthermore, with the ongoing push for sustainable practices, non-ionic polyacrylamide's role in water conservation and soil management will likely gain more prominence.
In conclusion, non-ionic polyacrylamide stands out as a multi-functional polymer with vast potential across various industries. Its unique properties and versatility make it an invaluable resource in water treatment, agriculture, biomedical applications, and more. As scientific advances continue to evolve, the scope of non-ionic polyacrylamide applications is expected to expand, paving the way for innovative solutions to contemporary challenges.
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride: High-Purity DisinfectantNewsAug.30,2025
-
2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid: Scale & CorrosionNewsAug.29,2025
-
Premium Isothiazolinones | Broad-Spectrum Biocidal SolutionsNewsAug.28,2025
-
LK-319 Special Scale And Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Plants: Advanced Solutions for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: Essential Chemical Solutions for Purification ProcessesNewsAug.22,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: Versatile Microbial Control Agents for Industrial and Consumer ApplicationsNewsAug.22,2025





