flocculation chemicals
Understanding Flocculation and Its Chemicals
Flocculation is a crucial process in water treatment, mining, and various industrial applications. It involves the agglomeration of particles to form larger clusters or flocs, allowing for easier removal and clarification of liquids. This process plays a pivotal role in purifying water, enabling the separation of solids from liquids, and enhancing the efficiency of various operations. Central to the flocculation process are the chemicals used to facilitate this agglomeration. In this article, we will explore the types, mechanisms, and applications of flocculation chemicals.
Types of Flocculation Chemicals
Flocculants can be broadly categorized into two groups inorganic and organic flocculants.
1. Inorganic Flocculants These are primarily metal salts, such as aluminum sulfate (alum), ferric chloride, and ferric sulfate. Inorganic flocculants work by neutralizing the surface charges of suspended particles, allowing them to come together and form larger aggregates. For example, aluminum sulfate is frequently used in drinking water treatment facilities for its efficiency in coagulating and settling small particles, making it easier to clarify water.
2. Organic Flocculants These are polymers that can be natural or synthetic. They include polyacrylamides, xanthan gum, and starch-based flocculants. Organic flocculants are usually more effective at very low concentrations and can enhance sedimentation rates significantly. Polyacrylamides, for example, are widely used in wastewater treatment due to their ability to form flocs over a broad range of conditions. They can come in cationic, anionic, or non-ionic forms, allowing for tailored applications depending on the nature of the suspended solids.
Mechanism of Flocculation
The flocculation process typically involves three key stages coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation.
1. Coagulation This initial stage is where flocculation chemicals neutralize the charges on suspended particles. As particles carry a negative charge, they repel each other, hindering aggregation. By adding a coagulant like aluminum sulfate, the electrical charges are neutralized, prompting particles to collide and bond.
2. Flocculation Next, the formation of flocs occurs, aided by gentle stirring or mixing. The flocculant molecules bridge multiple particles, creating larger aggregates. This phase relies on the size, concentration, and characteristics of the flocculant used.
flocculation chemicals
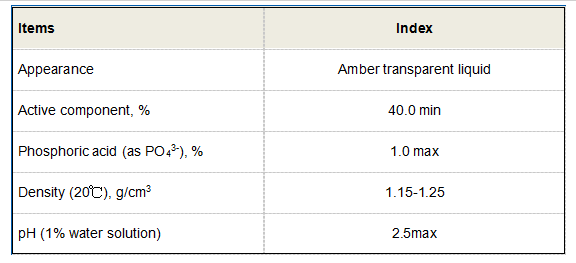
3. Sedimentation Finally, the larger flocs formed during flocculation settle at the bottom of the container or treatment basin, allowing for easy removal from the treated liquid. This process is essential for producing clear water in both industrial processes and municipal water systems.
Applications of Flocculation Chemicals
Flocculation chemicals find applications in various sectors
1. Water Treatment One of the most common applications is in municipal water treatment plants. Flocculants are critical for removing turbidity and contaminants from drinking water. They enhance sedimentation rates, reducing the need for extensive filtration processes and ensuring compliance with health standards.
2. Wastewater Treatment In industrial settings, flocculants help in the efficient processing of wastewater. By removing suspended solids and helping in the recovery of valuable resources, flocculation contributes significantly to environmental sustainability.
3. Mining Flocculation is utilized in the mining industry, particularly in the concentration of ores. Flocculants assist in separating valuable minerals from gangue, thereby improving metal recovery rates.
4. Paper Production In the paper industry, flocculation chemicals are essential in the pulp processing stage. They help in removing impurities, leading to higher quality paper products.
Conclusion
Flocculation is an indispensable process in various industries, underscored by the importance of flocculation chemicals. Whether through the use of inorganic salts or organic polymers, the effective removal of suspended solids enhances water clarity, waste management, and resource recovery. As industries continue to evolve, the development and application of more efficient and eco-friendly flocculants will remain a critical focus area, promising to contribute positively to our environment and health.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





