inhibitor water treatment
Understanding Inhibitors in Water Treatment
Water treatment processes are crucial for ensuring the purity and safety of water used for various applications, including drinking, irrigation, and industrial uses. One of the significant challenges faced in water treatment is the control of scale formation, corrosion, and biological growth in systems. This is where inhibitors, also known as water treatment chemicals, come into play. They are substances added to water to prevent unwanted reactions and to maintain the integrity of the system.
The Role of Inhibitors
Inhibitors work by targeting specific problems within water systems. For instance, scale inhibitors prevent the crystallization of minerals like calcium and magnesium, which, if left unchecked, can lead to scale buildup in pipes and equipment. This buildup not only hinders water flow and efficiency but also increases maintenance costs and decreases the lifespan of equipment.
Corrosion inhibitors, on the other hand, protect metal surfaces in contact with water. They form a protective layer on the metal, which prevents the oxidation process that can lead to rust and deterioration. This is particularly important in industrial settings where large pipelines and machinery are involved.
Biocides, another type of inhibitor, are used to control biological growth within water systems. Algae and bacterial growth can lead to biofilm formation, which can further contribute to corrosion and scale. By using biocides, water treatment facilities can keep these microorganisms in check, ensuring the water remains clean and safe for use.
Types of Inhibitors
Inhibitors can be categorized based on their specific functions
1. Scale Inhibitors Commonly used in cooling towers, boilers, and pipelines, these chemicals alter the crystal growth of minerals, making them less likely to form deposits. Examples include phosphonates and polyacrylic acids.
2. Corrosion Inhibitors These can be organic or inorganic compounds designed to protect metal surfaces. Common examples include phosphates, nitrites, and organic amines. Each type has its application depending on the water chemistry and metal type involved.
inhibitor water treatment
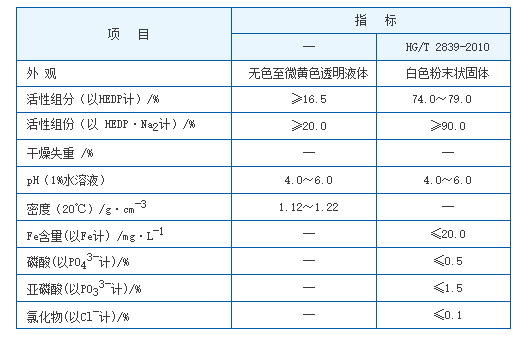
3. Biocides These are used to kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms. Chlorine, ozone, and various specialty biocides are commonly utilized in water treatment systems to prevent biological contamination.
Importance of Water Treatment Inhibitors
The significance of water treatment inhibitors cannot be overstated. They not only save costs associated with maintenance and repair but also enhance the efficiency of water systems. Systems protected by inhibitors typically experience fewer disruptions caused by scaling and corrosion, allowing for smoother and more efficient operation.
When considering the environmental impact, using inhibitors can also contribute to sustainability. Effective water treatment reduces the need for excessive chemical usage and minimizes waste discharge. Moreover, by prolonging the lifespan of equipment, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and use resources more cautiously.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, the use of inhibitors must be carefully managed. The wrong type or dosage can lead to inefficiencies or create new problems. For instance, some inhibitors may interact negatively with other chemicals in the system, leading to unforeseen consequences. Additionally, there are environmental concerns associated with certain biocides and chemicals, prompting a need for more eco-friendly alternatives.
It is essential for water treatment facilities to conduct thorough assessments of their water systems. This includes testing water chemistry, understanding the types of materials present in the system, and determining the specific challenges faced. Consulting with experts in water treatment can provide valuable insights into selecting the most appropriate inhibitors for specific situations.
Conclusion
Inhibitors play a vital role in modern water treatment, addressing challenges related to scale, corrosion, and biological contamination. Their effective use can enhance system efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and contribute to environmental sustainability. However, careful selection and management of these chemicals are necessary to ensure that they provide the intended benefits without causing additional issues. As technology and research continue to advance, the development of more effective and eco-friendly inhibitors will be essential for the future of water treatment.
-
2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid: Scale & CorrosionNewsAug.29,2025
-
Premium Isothiazolinones | Broad-Spectrum Biocidal SolutionsNewsAug.28,2025
-
LK-319 Special Scale And Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Plants: Advanced Solutions for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: Essential Chemical Solutions for Purification ProcessesNewsAug.22,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: Versatile Microbial Control Agents for Industrial and Consumer ApplicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor: Key Solutions for Water System Scale PreventionNewsAug.22,2025





