non ionic polyacrylamide
The Versatility of Non-Ionic Polyacrylamide
Non-ionic polyacrylamide (NIPAM) is a synthetic polymer that has gained significant attention in various fields due to its exceptional properties and versatility. Characterized by its non-ionic nature, this polymer differs from its ionic counterparts by the absence of charged groups, making it particularly useful in applications where charge neutrality is desired.
The Versatility of Non-Ionic Polyacrylamide
In medical applications, NIPAM’s biocompatibility makes it suitable for drug delivery systems. By utilizing its ability to swell and shrink in response to environmental stimuli, NIPAM hydrogels can effectively control the release of therapeutic agents, ensuring a sustained release over extended periods. This property is particularly beneficial in targeted drug therapies, where precise dosage control is critical for maximizing therapeutic effects while minimizing side effects.
non ionic polyacrylamide
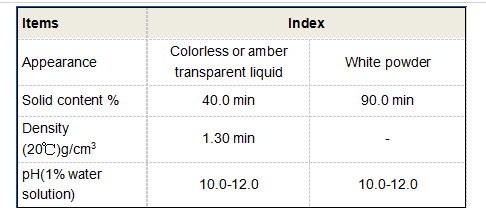
Moreover, non-ionic polyacrylamide is widely used in the field of wastewater treatment. Its polymeric structure enables it to act as a flocculant, helping to aggregate and precipitate suspended particles in wastewater. This results in clearer effluent and better overall quality of treated water, contributing to environmental sustainability and public health.
Another important aspect of NIPAM is its role in various industrial applications, including papermaking, textile, and oil recovery. In the paper industry, it enhances the retention of fillers and improves the paper’s strength. In textile processing, it can be employed as a thickener for dyes, ensuring better color retention and uniformity. Additionally, in enhanced oil recovery, non-ionic polyacrylamide improves the flow of oil through porous rock formations, increasing extraction efficiency.
The ongoing research into the modifications and enhancements of non-ionic polyacrylamide continues to unlock new potential applications across various disciplines. Its unique characteristics and adaptability make it a vital polymer in both current and future advancements, paving the way for innovations in technology, medicine, and environmental protection. As industries seek sustainable and efficient solutions, non-ionic polyacrylamide stands out as a promising material that meets diverse challenges head-on.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





