scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitor Chemicals An Overview
In various industrial applications, particularly in sectors like oil and gas, power generation, and water treatment, the issues of scale formation and corrosion are of paramount concern. Scale refers to the buildup of minerals on surfaces, while corrosion involves the degradation of materials, often metals, due to chemical reactions with their environment. Both phenomena can lead to significant operational challenges, including reduced efficiency, increased maintenance costs, and even catastrophic failures. To mitigate these issues, the use of scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals has become essential.
Understanding Scale Formation
Scale primarily forms when dissolved minerals, such as calcium and magnesium, precipitate out of solution due to changes in temperature, pressure, or chemical composition of water. This precipitation can result in the formation of hard deposits within pipes, boilers, and heat exchangers. These deposits can severely hinder the flow of fluids, reduce heat transfer efficiency, and lead to overheating, which can ultimately cause equipment failures.
To combat scale, industries employ scale inhibitors, which are chemical substances that interfere with the crystallization processes of minerals. These inhibitors can work by several mechanisms, including dispersing particles, sequestering ions, and modifying the crystal growth of scale-forming compounds. Common scale inhibitors include organophosphates, polyacrylates, and phosphate esters. Choosing the right scale inhibitor often depends on factors such as the type of scale present, water chemistry, and specific operational conditions.
The Corrosion Challenge
Corrosion is an electrochemical process that consumes metals, leading to structural weakness and failure. In industrial systems, corrosion can be triggered by factors including the presence of oxygen, water, and aggressive ions such as chlorides. The consequences of corrosion are profound, often resulting in expensive downtime, safety risks, and environmental hazards due to leaks and failures.
scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals
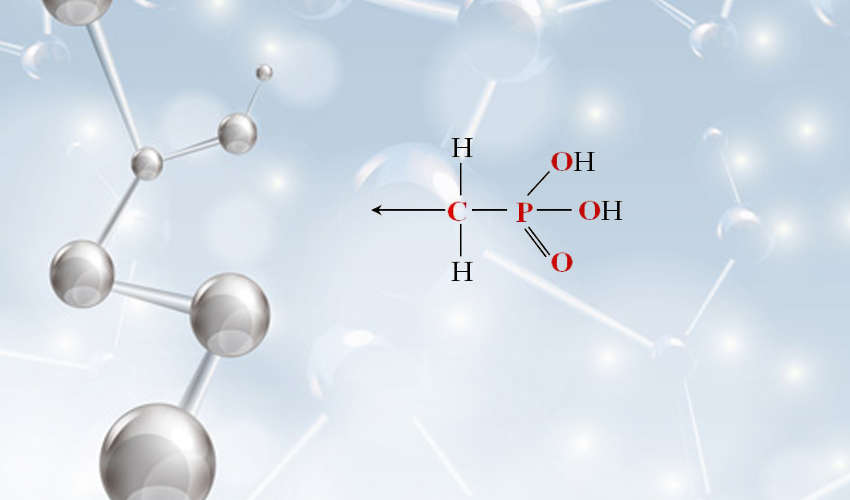
To prevent corrosion, industries utilize corrosion inhibitors, which can be categorized into several types, including anodic inhibitors, cathodic inhibitors, and passivating agents. Anodic inhibitors work by forming a protective coating on the metal surface, while cathodic inhibitors alter the electrochemical reactions occurring on the metal surface. Passivating agents enhance the formation of a passive film on the metal, further protecting it from corrosive environments.
Commonly used corrosion inhibitors include amines, phosphates, and to a lesser extent, organic compounds such as azoles. Selecting a corrosion inhibitor requires careful consideration of the metal involved, the corrosive environment, and operational conditions. For instance, amine-based inhibitors are often used in oil and gas applications due to their effectiveness in sour environments.
Integrated Approaches
Recent advancements in the field of chemistry and materials science have led to the development of integrated approaches that combine both scale and corrosion inhibition properties into a single formulation. These dual-action chemicals are particularly advantageous in streamlining treatment processes and reducing chemical usage while enhancing overall system efficiency.
Conclusion
The effective management of scale and corrosion is critical for the longevity and efficiency of industrial systems. By employing scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals, facilities can achieve significant reductions in maintenance costs, avoid unplanned downtimes, and improve overall operational efficiency. As industries continue to innovate and evolve, ongoing research into more effective, eco-friendly, and cost-efficient inhibitors remains a priority. The combined efforts in developing advanced chemical formulations will play a vital role in ensuring that industrial operations remain sustainable while addressing the persistent challenges posed by scale and corrosion.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





