Exploring the Properties and Applications of Partially Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide in Various Industries
Partially Hydrolysed Polyacrylamide Properties, Applications, and Environmental Impact
Partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide (PHPA) is a synthetic polymer that plays a crucial role in various industrial applications, particularly in the fields of water treatment, agriculture, and petroleum extraction. Its unique properties stem from the partial hydrolysis of polyacrylamide, which enhances its effectiveness as a flocculant, soil conditioner, and viscosity enhancer.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide is derived from polyacrylamide through a controlled hydrolysis process. This structure consists of acrylamide units, where a portion of the amide groups is converted to carboxyl groups. The result is a water-soluble polymer with a balance of cationic and anionic properties, which significantly influences its interactions with other substances.
The degree of hydrolysis determines many of PHPA's properties, including its solubility, molecular weight, and reactivity. The partially hydrolysed nature of the polymer allows for improved water retention and nutrient absorption in soils, making it a valuable additive in agricultural practices. Additionally, its flocculating properties are vital in enhancing sedimentation processes in water treatment facilities, where clarity and purity are paramount.
Applications
1. Water Treatment In the realm of wastewater management, PHPA is extensively used as a flocculant. It aids in aggregating suspended particles, allowing for their easier removal during sedimentation processes. This function is vital for treating municipal and industrial wastewater, ensuring that the final output meets stringent environmental regulations.
2. Agriculture In agriculture, PHPA serves as a soil conditioner. By improving soil structure, it enhances water retention and reduces erosion, consequently promoting healthier crop yields. Its ability to bind with moisture around plant roots prevents drought conditions, making it an essential component in arid and semi-arid regions.
partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide
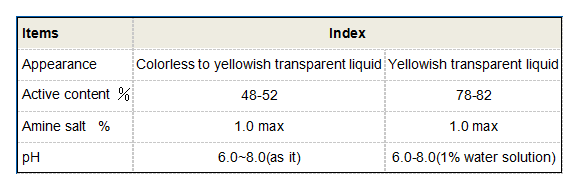
3. Oil and Gas Industry PHPA is also widely utilized in the petroleum industry, particularly in drilling fluids. Its thickening properties help maintain the stability of boreholes and improve the efficiency of drilling operations. Additionally, PHPA can assist in enhancing oil recovery by improving the mobility of oil within reservoirs.
Environmental Considerations
While the benefits of PHPA are manifold, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. The production and degradation of synthetic polymers often raise concerns regarding toxicity and pollution. Although PHPA is generally considered safe for use in various applications, its long-term environmental effects warrant further research.
Studies have shown that PHPA is biodegradable under specific conditions, yet its persistence in the environment can be a concern, especially in aquatic ecosystems. The leaching of polymer fragments can potentially harm aquatic life and disrupt ecological balances. Therefore, careful management and proper application techniques are essential to mitigate possible adverse effects.
Conclusion
Partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide is a versatile polymer that has carved a niche for itself across multiple industries due to its unique properties and functionalities. Its applications in water treatment, agriculture, and the oil industry highlight its significance in addressing modern challenges related to resource management and environmental sustainability.
However, as with any synthetic substance, it is crucial to weigh the benefits against potential environmental impacts. Ongoing research and advancements in polymer science will likely lead to the development of improved formulations that balance efficiency with ecological safety. By adopting sustainable practices and using PHPA judiciously, industries can harness its advantages while minimizing risks to our planet.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





