polyacrylamide uses
Versatile Applications of Polyacrylamide A Multifunctional Polymer
Polyacrylamide, a synthetic polymer, has garnered significant attention in various industries due to its versatile properties and applications. Its ability to form hydrogels, coupled with its excellent water-absorbing and binding capabilities, makes polyacrylamide an invaluable material in several fields, including agriculture, water treatment, papermaking, and biomedical applications.
1. Agricultural Applications
In agriculture, polyacrylamide plays a crucial role in enhancing soil quality and improving water retention. As a soil conditioner, it helps reduce water runoff and soil erosion while increasing the soil's ability to retain moisture. The incorporation of polyacrylamide into the soil can lead to better crop yields, especially in arid and semi-arid regions where water scarcity is a significant concern. Additionally, polyacrylamide can be utilized in controlled-release fertilizers, providing a slow and steady supply of nutrients to plants, further enhancing agricultural productivity.
2. Water Treatment
Another significant use of polyacrylamide is in water treatment processes. It acts as a flocculant, helping to agglomerate suspended particles in water, thereby facilitating their removal. This property is particularly important in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, where polyacrylamide aids in clarifying water by increasing the size of particles, making them easier to filter out. Its effectiveness in removing contaminants such as heavy metals and organic compounds makes polyacrylamide an essential component in achieving water quality standards and ensuring environmental safety.
polyacrylamide uses
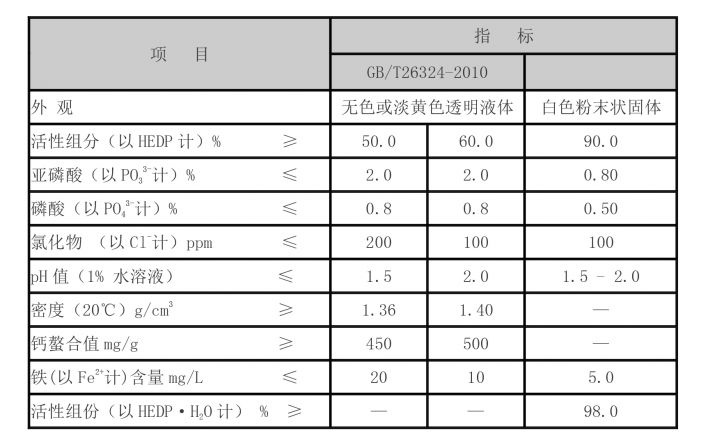
In the papermaking industry, polyacrylamide serves multiple functions, primarily as a retention aid and a dry strength agent. Its ability to bind fibers and fillers together increases the efficiency of the papermaking process, resulting in higher quality paper products. By improving fiber retention during the paper formation process, polyacrylamide helps reduce raw material costs and water usage. Furthermore, the addition of polyacrylamide enhances the strength and durability of paper, making it suitable for a variety of applications, from packaging to stationery.
4. Biomedical Applications
The biomedical field has also benefitted from the unique properties of polyacrylamide. Its biocompatibility and ability to form hydrogels make it an excellent candidate for drug delivery systems and tissue engineering. Polyacrylamide-based hydrogels can encapsulate drugs, providing controlled release over time, which is crucial for improving the efficacy of treatments. Additionally, these hydrogels can serve as scaffolds in tissue engineering, supporting cell growth and differentiation, and promoting the regeneration of damaged tissues. Researchers continue to explore innovative applications of polyacrylamide in biomedicine, paving the way for advancements in medical treatments and therapies.
5. Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry also utilizes polyacrylamide extensively, particularly in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques. In this context, polyacrylamide is employed as a thickening agent to modify the viscosity of water injected into oil reservoirs. This adjustment improves the efficiency of oil extraction by ensuring that water can displace the oil more effectively, thereby increasing the overall yield from existing wells. The use of polyacrylamide in EOR not only enhances recovery rates but also minimizes environmental impacts by reducing the need for more invasive extraction methods.
Conclusion
Polyacrylamide's diverse range of applications illustrates its importance across various industries. From agriculture and water purification to papermaking and biomedical uses, this multifunctional polymer demonstrates unique properties that contribute to efficiency, sustainability, and innovation. As research continues to explore new applications and improve existing technologies, polyacrylamide will likely remain a critical material in addressing contemporary challenges in various sectors. As industries evolve and environmental concerns intensify, the role of polyacrylamide will undoubtedly expand, proving its worth as a vital resource for modern society.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





