Exploring the Role of HEDP in Enhancing Soap Formulations and Cleaning Efficacy
The Role of HEDP in Soap Production
HEDP, or 1-Hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid, is a versatile chemical that plays a pivotal role in various industrial applications, including the production of soaps and detergents. Its unique properties make it a valuable ingredient in formulations aimed at enhancing the effectiveness and stability of cleaning products. Understanding the significance of HEDP in soap production offers insights into its chemical characteristics and benefits.
Chemical Properties of HEDP
HEDP is a phosphonate that has a high affinity for metal ions. Its structure allows it to chelate (bind) calcium, magnesium, and other divalent metal ions, which are often present in hard water. This chelation ability is crucial because hard water can impede the performance of soaps and detergents by forming insoluble salts that reduce lathering and cleaning efficiency. By sequestering these metal ions, HEDP enhances the stability and effectiveness of soap formulations.
Application in Soap Production
In the formulation of soaps, HEDP is primarily used as a water softener. When added to a soap product, it helps to prevent the precipitation of mineral salts, ensuring that the active cleaning agents remain available to interact with dirt and grease. This results in soaps that not only lather well but also maintain their cleansing power, even in challenging water conditions.
hedp in soap
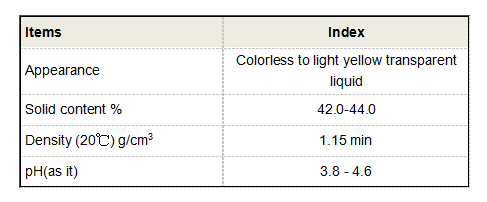
Moreover, HEDP contributes to the preservation of soap products. Its ability to chelate metal ions also means that it can inhibit the catalytic activity of these ions, which can lead to the degradation of active ingredients over time. This makes soap formulations more stable and extends their shelf life, ultimately benefiting both manufacturers and consumers.
Environmental Considerations
One of the critical advantages of HEDP is its relatively low environmental impact compared to traditional phosphates used in cleaning products. While phosphates have been associated with eutrophication in aquatic environments, HEDP is considered to have a lower propensity to contribute to these issues. As a result, many manufacturers are turning to HEDP as a more environmentally friendly alternative in their soap formulations. This shift aligns with the increasing demand for sustainable and eco-conscious products in the market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HEDP plays a crucial role in the soap production process. Its capabilities as a water softener and stabilizing agent enhance the performance and longevity of soap products, making it an indispensable ingredient in the industry. As the focus on sustainability continues to rise, HEDP provides a viable solution that meets both performance and environmental criteria. Manufacturers who leverage the benefits of HEDP in their soap formulations can better meet consumer demands for high-quality, effective, and eco-friendly cleaning products. The ongoing research and development in the field of cleaning agents suggest that HEDP's role may expand further, promising even more innovative solutions in the future.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





