butane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
The Role of Butane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid in Organic Chemistry
Butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid—often referred to as citric acid or in more technical settings as tricarballylic acid—plays a significant role in organic chemistry and various industrial applications. This organic compound, characterized by three carboxylic acid groups located at the first, second, and fourth carbon positions of a butane backbone, is widely recognized for its multifunctionality and versatility.
The Role of Butane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid in Organic Chemistry
In biochemistry, this compound is integral to the Krebs cycle (or citric acid cycle), a vital metabolic pathway present in aerobic organisms. During this cycle, it plays a crucial role in the oxidation and conversion of nutrients into energy. The efficient conversion of energy is essential for living organisms, highlighting the importance of butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid as more than just a chemical entity but as a biological necessity.
butane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
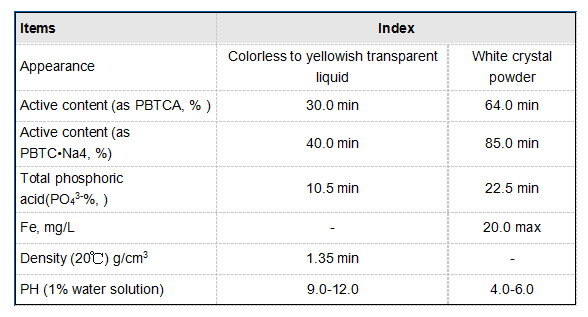
Moreover, its applications extend beyond metabolism. In the food industry, citric acid is well-known for its sour taste and preservative qualities. As a natural preservative, it helps to enhance flavors, stabilize products, and extend shelf life. This multi-faceted utilization showcases the compound's significance in both scientific and practical domains.
In addition to its natural roles, butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid has garnered attention in modern research focused on sustainable practices and eco-friendly chemical processes. The study of its derivatives and their potential applications in biodegradable materials signifies a shift towards greener chemistry. Researchers are increasingly exploring its use in synthesizing polymers and solvents, aiming to reduce reliance on petroleum-based products.
In conclusion, butane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid serves as a prime example of the intersection between organic chemistry and practical applications. Its structural characteristics make it a vital compound in both biological processes and industrial applications, affirming its place as an essential substance in a wide range of fields. As research progresses, the potential for new applications and sustainable uses of this compound continues to expand, promising exciting advancements in the future.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





