industrial flocculant
Understanding Industrial Flocculants A Key Component in Water Treatment
Flocculants play a crucial role in various industrial processes, particularly in water treatment and wastewater management. These chemical substances are designed to promote the clumping or flocculation of fine particles, facilitating their removal from liquid media. The importance of flocculants extends beyond just enhancing water clarity; they are also vital for environmental protection and sustainability in industrial operations.
What are Flocculants?
Flocculants are typically large molecules that can be either natural or synthetic. Natural flocculants are derived from plant extracts, such as alginate from seaweed or starch derivatives, while synthetic flocculants are often polyacrylamides or copolymers of various monomers. These substances function by bridging the gaps between smaller particles, forming larger aggregates or flocs that can then be easily separated from the liquid through sedimentation, filtration, or flotation.
Applications in Water Treatment
One of the primary applications of flocculants is in water treatment plants where they are used to clarify drinking water. During the treatment process, raw water can contain various contaminants such as silt, clay, organic matter, and microorganisms. By adding flocculants, these impurities can be efficiently agglomerated and removed, resulting in cleaner water. This is particularly important as global water sources become increasingly strained due to growing populations and pollution.
Flocculants are not limited to drinking water; they also play a significant role in wastewater treatment. Industries such as mining, food and beverage, and petrochemicals utilize flocculants to treat effluents before releasing them back into the environment. In these processes, flocculants help reduce the volume of sludge, making disposal easier and more economical while ensuring that pollutants are adequately removed to meet regulatory standards.
Types of Flocculants
Flocculants can be classified into several categories based on their charge properties
industrial flocculant
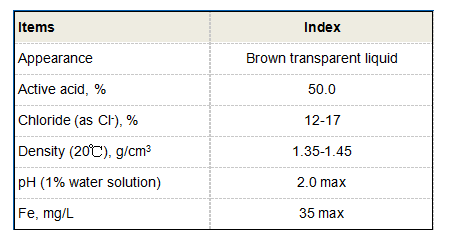
1. Anionic Flocculants These carry a negative charge and are effective in treating wastewater with positively charged particles, often used in mineral processing. 2. Cationic Flocculants With a positive charge, these flocculants are commonly used in paper manufacturing and to assist in the treatment of municipal wastewater that contains organic material.
3. Non-ionic Flocculants These have no charge and are generally suitable for a broader range of applications, providing flexibility in treating varying types of industrial waste.
4. Natural Flocculants As mentioned earlier, these are derived from natural resources and are increasingly popular due to their lower environmental impact.
Environmental Considerations
The use of flocculants also brings environmental considerations to light. While many synthetic flocculants are highly effective, there are concerns regarding their degradation and potential toxicity to aquatic life. Hence, there is a growing trend towards the use of biodegradable, natural flocculants as sustainable alternatives. Research in this area is vibrant, focusing on developing new formulations that maintain efficiency while reducing harmful environmental impacts.
Future Trends
As industries strive for improved efficiency and sustainability, the demand for effective flocculants is expected to rise. Innovations in polymer chemistry and environmental science will likely lead to the development of new flocculants designed to perform better with fewer adverse effects. Furthermore, as regulations around water treatment become stricter globally, the role of flocculants in achieving compliance will become even more significant.
In conclusion, industrial flocculants are indispensable components in water treatment processes. They enhance the efficiency of contaminant removal, reduce waste management costs, and help industries meet environmental regulations. As the world increasingly turns its attention to sustainability, the future of flocculants may hold more eco-friendly solutions that will serve both industrial needs and environmental protection.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





