Poly Aluminium Chloride (PAC) for Water Treatment | Effective Solutions
The Uses of Poly Aluminium Chloride in Water Treatment
Poly Aluminium Chloride (PAC) is a widely used chemical coagulant in water treatment processes, particularly in the purification of drinking water, wastewater treatment, and various industrial applications. Its unique properties make it a preferred choice due to its effectiveness in removing contaminants, improving water clarity, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
What is Poly Aluminium Chloride?
PAC is an inorganic polymer that consists of aluminium salts that have been polycondensed. It is usually available in either liquid or solid forms and has a range of molecular weights and basicity levels. The structure of PAC enables it to form larger and more stable flocs compared to traditional coagulants like alum (aluminium sulfate), making it highly effective in various water treatment scenarios.
Mechanism of Action
The effectiveness of PAC in water treatment primarily hinges on its coagulant properties. When PAC is added to water, it undergoes hydrolysis to form aluminium hydroxide, which then precipitates out of the solution. This process attracts and binds with suspended solids, colloidal particles, and organic matter in the water, forming larger aggregates known as flocs. These flocs can then be easily removed from the water through sedimentation or filtration.
Applications in Drinking Water Treatment
poly aluminium chloride uses in water treatment
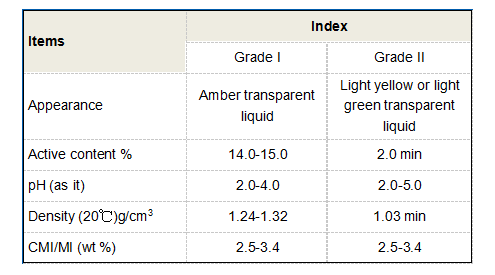
In drinking water treatment facilities, PAC is used to clarify water by removing turbidity and harmful microorganisms. The efficiency of PAC in a wide pH range (4 to 10) makes it versatile for different water quality conditions. Additionally, PAC has lower residual aluminium compared to traditional alum, which is a critical advantage for health and safety reasons, particularly in drinking water applications. This characteristic not only ensures cleaner water but also reduces the risk of health issues associated with excessive aluminium exposure.
Wastewater Treatment
PAC is also extensively utilized in wastewater treatment processes. Its application helps in the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants, heavy metals, and phosphates from effluent streams. The floc-forming ability of PAC enhances the decantation process, improving separation efficiency during clarifiers and sludge thickening. By using PAC, wastewater treatment plants can achieve higher quality effluent standards, thus playing a crucial role in protecting the environment and water bodies from pollution.
Industrial Uses
Beyond municipal water treatment, PAC is employed in various industrial applications, including paper manufacturing, textile processing, and food production. In these industries, PAC serves multiple purposes such as enhancing filtration processes, improving product quality, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards for waste discharge.
Conclusion
In summary, Poly Aluminium Chloride is a versatile and effective coagulant that plays a significant role in both drinking water purification and wastewater treatment. Its ability to form larger flocs, lower environmental impact, and versatility across various pH levels make it an indispensable tool in the water treatment arsenal. As water quality standards continue to tighten globally, the demand for efficient coagulants like PAC is expected to grow, emphasizing its importance in sustainable water management practices. By ensuring cleaner water for communities and minimizing adverse environmental impacts, PAC remains a cornerstone in modern water treatment technologies.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





