Understanding Scale Formation and the Role of Corrosion Inhibitor Chemicals in Industrial Applications
The Importance of Scale and Corrosion Inhibitor Chemicals in Industrial Applications
In various industrial sectors, particularly in oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing, the presence of scale and corrosion poses significant challenges. These issues can lead to reduced efficiency, increased maintenance costs, and even catastrophic equipment failures. To combat these problems, scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals play a crucial role. This article delves into the significance of these chemicals, their mechanisms of action, and their applications across various industries.
Understanding Scale and Corrosion
Scale refers to the buildup of mineral deposits on equipment surfaces, often arising from water containing high concentrations of dissolved minerals like calcium, magnesium, and silica. These deposits can clog pipes, reduce heat transfer efficiency in boilers, and affect the overall performance of systems.
Corrosion, on the other hand, is the gradual destruction of materials, usually metals, due to chemical reactions with their environment. Common causes of corrosion include exposure to moisture, acids, and salts, which can lead to pitting, rusting, and eventual failure of critical components.
The Role of Inhibitor Chemicals
Scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals are specifically designed to prevent or mitigate these detrimental effects. Their primary function is to inhibit the formation of scale and to protect metal surfaces from corrosion. They accomplish this through various mechanisms, including
1. Threshold Inhibition Some inhibitors can alter the solubility of scale-forming minerals, allowing them to remain in solution rather than precipitating and forming scale.
2. Film Formation Many corrosion inhibitors work by forming a protective layer on the surface of metal. This film acts as a barrier between the metal and corrosive agents, thus minimizing corrosion rates.
scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals
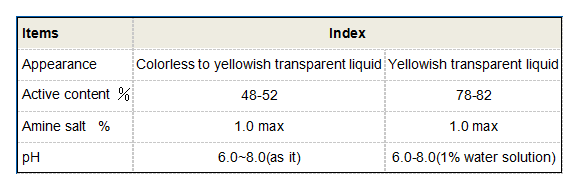
4. Biological Control In some cases, inhibitors also address biological fouling caused by microorganisms in water systems, further enhancing their effectiveness.
Applications of Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors
The applications of these inhibitors span a variety of industries
1. Oil and Gas Industry In this sector, the presence of scale and corrosion can lead to significant production losses and safety hazards. Inhibitors are used in pipelines, tanks, and drilling fluids to prolong the life of equipment and ensure efficient operations.
2. Water Treatment In municipal and industrial water treatment facilities, scale and corrosion inhibitors are crucial to maintain the integrity of distribution systems, boilers, and cooling towers. They help ensure that systems operate efficiently and safely, reducing maintenance downtime and costs.
3. Power Generation In thermal and nuclear power plants, where water is a primary component of the cooling systems, scale and corrosion can compromise efficiency. Inhibitors are essential to maintaining the performance of boilers and heat exchangers, ultimately contributing to the reliability of energy production.
4. Manufacturing Industries involved in metal fabrication and production often encounter issues related to corrosion. The use of inhibitors can enhance the durability of products and reduce costly repairs and replacements.
Conclusion
The significance of scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals cannot be overstated in the context of modern industrial operations. By effectively preventing scale buildup and corrosion, these chemicals not only protect infrastructure and equipment but also contribute to improved operational efficiency and reduced costs. As industries evolve and the demand for reliable and sustainable operations increases, the role of these inhibitors will continue to expand, underscoring their essential place in maintaining the integrity and functionality of systems across various sectors. As we look forward, advancements in inhibitor formulations and application techniques will further enhance their effectiveness, paving the way for safer and more efficient industrial processes.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





