Synthesis and Applications of Polyepoxysuccinic Acid in Modern Chemistry
Polyepoxysuccinic Acid An Innovative Biopolymer with Versatile Applications
Polyepoxysuccinic acid (PESA) is an innovative biopolymer that has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its environmentally friendly properties and versatile applications. Deriving from renewable resources, PESA is a water-soluble polymer that exhibits a range of functionalities suitable for various industries, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and materials science.
Chemical Structure and Properties
PESA is synthesized through the polymerization of epoxysuccinic acid, a compound that is characterized by its unique structure featuring carboxylic acid groups and epoxide functionalities. This structure allows PESA to exhibit excellent chelating properties, making it effective in binding metal ions. Its water solubility enhances its applicability in various formulations and processes, particularly in aqueous environments.
The polymer's inherent stability and compatibility with other compounds make it an attractive choice for developing biodegradable and non-toxic products. Furthermore, PESA exhibits low toxicity profiles, reducing concerns related to environmental pollution and human health risks commonly associated with synthetic polymers.
Applications in Agriculture
One of the most promising applications of polyepoxysuccinic acid is in the agricultural sector
. PESA can be used as a biodegradable agent in fertilizers, helping to improve nutrient absorption and reduce the leaching of essential minerals. By chelating metal ions, PESA enhances the availability of micronutrients to plants, promoting healthier growth and increasing crop yields.Moreover, PESA can act as a surfactant and dispersant, facilitating the formulation of pesticide and herbicide products. Its ability to improve the stability and effectiveness of agrochemicals ensures better penetration and adherence to plant surfaces, which ultimately leads to improved pest control and reduced chemical runoff into the environment.
polyepoxysuccinic acid
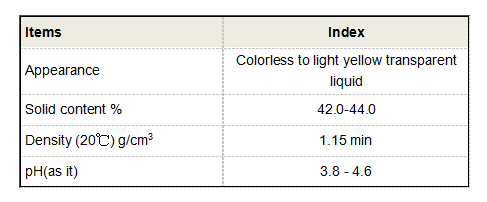
Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications
In the pharmaceutical industry, the coupler properties of PESA have sparked interest for drug delivery systems. Its biocompatibility allows for the encapsulation of therapeutic agents, facilitating controlled release and improving the efficacy of medications. For instance, PESA-based formulations can target specific tissues, reducing systemic side effects associated with traditional drug therapies.
Furthermore, PESA serves as a promising candidate for biomedical applications, including tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Its ability to form hydrogels and scaffolds provides a conducive environment for cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation, essential for developing artificial tissues and organs.
Material Science and Sustainable Practices
The material science sector is another area where PESA shows great promise. Its properties can be harnessed to develop biodegradable plastics, coatings, and adhesives that reduce reliance on petroleum-based resources. With increasing global emphasis on sustainability and reducing plastic pollution, PESA offers a viable alternative that aligns with eco-friendly practices.
Research is ongoing to optimize the synthesis and functional properties of PESA to broaden its applicability further. Innovations such as blending PESA with other biodegradable materials could lead to composite materials with enhanced mechanical strength and durability, which are essential for various industrial applications.
Conclusion
Polyepoxysuccinic acid stands out as an innovative biopolymer with the potential to transform multiple industries by providing sustainable and eco-friendly solutions. Its versatile applications in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and material science highlight its unique properties and functionality. As research continues to explore and expand the use of PESA, it is poised to play a significant role in addressing the pressing challenges associated with environmental sustainability and resource management.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





