Properties and Applications of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water Treatment Processes
Poly Aluminum Chloride An Essential Coagulant in Water Treatment
Poly aluminum chloride (PAC) is an inorganic polymer that has gained significant attention in the field of water treatment and purification. As a coagulant, PAC is widely used in various applications, including drinking water, wastewater treatment, and industrial processes. Its effectiveness and versatility make it a fundamental component in ensuring clean and safe water for communities and industries alike.
Composition and Properties
Poly aluminum chloride is synthesized through the reaction of aluminum hydroxide with hydrochloric acid, resulting in a polymeric aluminum compound. The basic chemical formula can be represented as Aln(OH)mCl3n-m, where 'n' is the degree of polymerization, and 'm' refers to the number of hydroxyl ions. This unique composition gives PAC superior coagulating properties compared to traditional coagulants such as aluminum sulfate and ferric chloride.
One of the standout characteristics of PAC is its ability to work effectively across a wide pH range, typically between 5.0 and 9.0. This adaptability allows it to be used in various water quality situations without significant adjustments to pH levels. Additionally, PAC has a higher charge density, which enhances its interaction with suspended particles in water, leading to better coagulation and flocculation processes.
Mechanism of Action
The primary function of poly aluminum chloride in water treatment is to remove turbidity and other contaminants from the water
. When PAC is added to water, it dissociates into aluminum ions and hydroxyl ions, which then neutralize the negative charges on suspended particles, such as silt, clay, and organic matter. This neutralization leads to the aggregation of particles into larger flocs, which can then be easily removed through sedimentation or filtration.poly aluminum chloride
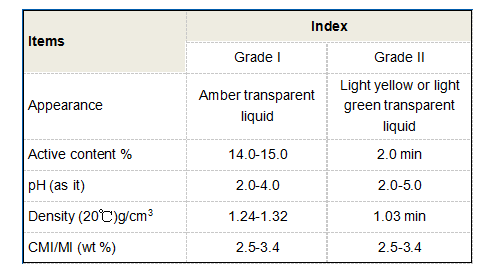
PAC’s ability to form a strong and dense floc is particularly beneficial for treating water with high levels of turbidity, color, and suspended solids. The resultant floc aggregates also settle quickly, thus reducing the time required for clarification processes, which is a critical factor in large-scale water treatment facilities.
Advantages of Using PAC
The use of poly aluminum chloride offers numerous advantages over traditional coagulants. First and foremost, PAC is highly efficient, often requiring lower doses than aluminum sulfate to achieve similar or better results. This not only leads to cost savings but also results in reduced sludge production during the treatment process.
Moreover, PAC is known for its ability to enhance the overall performance of water treatment plants. It has been found to improve the removal of a broader range of contaminants, including organic materials and pathogens, thereby contributing to the production of high-quality drinking water.
Another significant advantage of PAC is its lower environmental impact. It is less likely to cause environmental harm compared to some conventional coagulants. The reduced volume of sludge generated allows for easier management and disposal, addressing concerns regarding the disposal of residuals from treatment processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, poly aluminum chloride is a vital player in modern water treatment practices. Its effectiveness, cost-efficiency, and environmental benefits make it an attractive alternative to traditional coagulants. As the demand for clean and safe water continues to grow worldwide, the role of PAC in facilitating efficient water purification processes will remain indispensable. Whether in municipal water treatment facilities or industrial applications, poly aluminum chloride is set to continue making significant contributions to the field of water quality management.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





