cross linked polyacrylamide
Cross-linked polyacrylamide (CLPA) has gained significant attention in various fields, including materials science, biotechnology, and environmental engineering, due to its unique properties and versatile applications. As a synthetic polymer, polyacrylamide is formed by the polymerization of acrylamide monomers, and the introduction of cross-linking agents results in a three-dimensional network structure that enhances its mechanical strength and stability.
.
In the field of biotechnology, CLPA hydrogels can serve as scaffolds for cell culture, providing a supportive environment for tissue engineering. Their ability to mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM) in biological tissues makes them suitable for regenerative medicine applications. Additionally, cross-linked polyacrylamide can be modified with bioactive substances to enhance cell adhesion and proliferation, further improving its functionality in biomedical applications.
cross linked polyacrylamide
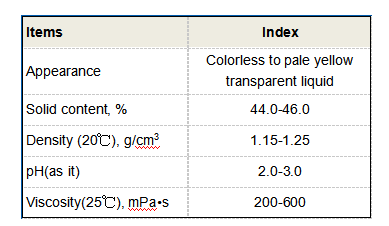
Furthermore, CLPA is employed in water treatment processes due to its effectiveness in removing pollutants. Its high absorption capacity and ability to form gels allow it to trap heavy metals and other contaminants, making it a valuable material for environmental remediation. The cross-linked structure also imparts stability, enabling the material to function in various environmental conditions without significant degradation.
The synthesis of cross-linked polyacrylamide can be tailored to achieve specific properties, such as varying degrees of cross-linking, pore size, and mechanical strength. This adaptability allows researchers to design CLPA materials that meet the requirements of specific applications, whether in the pharmaceutical industry or environmental science.
In conclusion, the versatility of cross-linked polyacrylamide makes it a highly promising material across a range of disciplines. Its unique combination of mechanical strength, hydrophilicity, and biocompatibility opens new avenues for innovation in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and environmental remediation. As research continues to explore its potential, it is likely that CLPA will play an increasingly important role in addressing modern challenges in healthcare and environmental sustainability.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





