Polyaluminium Chloride Water Treatment Solutions
The Role of Polyaluminium Chloride in Water Treatment
Water treatment is a critical process aimed at providing safe drinking water and ensuring effective wastewater disposal. One of the most significant substances used in this process is Polyaluminium Chloride (PAC). This chemical compound has gained popularity within the water treatment industry due to its efficiency, versatility, and environmental friendliness.
Polyaluminium chloride is a type of aluminium-based coagulant that is utilized primarily in the clarification and purification of water. It is derived from the neutralization of aluminium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid, resulting in a high molecular weight polymer. The unique structure of PAC allows it to bind effectively with impurities in water, making it an ideal agent for coagulation and flocculation processes.
One of the essential functions of PAC in water treatment is its ability to remove suspended solids and colloids from water. When introduced into contaminated water, PAC interacts with negatively charged particles, neutralizing their charges and causing them to agglomerate into larger clusters. These clusters, or flocs, can then be easily removed from the water through sedimentation or filtration processes. This mechanism is particularly beneficial in treating surface water sources, which often contain a high concentration of organic matter and pathogens.
PAC is favored over traditional coagulants like aluminium sulphate due to several advantages. Firstly, it operates effectively over a wider pH range, allowing for greater flexibility in different water treatment scenarios. Moreover, PAC typically requires lower dosages compared to other coagulants, resulting in reduced chemical costs and less waste generation. This reduction in waste is not only economically beneficial but also enhances the sustainability of the water treatment process.
polyaluminium chloride water treatment
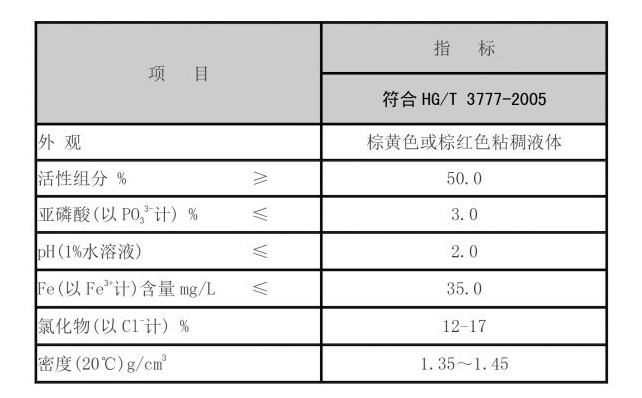
Furthermore, using PAC can lead to improved water quality. The flocs formed are generally larger and more buoyant, which facilitates easier removal during the sedimentation process. This results in clearer water with lower levels of residual contaminants, leading to improved aesthetic qualities and safety for consumers. Additionally, PAC produces fewer residual aluminum ions in treated water compared to other aluminium coagulants, which is an essential consideration in terms of human health and environmental impact.
The use of PAC in water treatment systems is applicable across various settings, including municipal drinking water plants, industrial wastewater facilities, and treatment processes for agricultural runoff. Its effectiveness and ease of handling make it a popular choice for water treatment professionals worldwide.
However, the implementation of PAC must be carefully monitored to ensure optimal results. Factors such as dosage, pH levels, and water temperature can significantly influence the coagulation process. Therefore, regular testing and adjustments are necessary to maintain efficient treatment and achieve regulatory compliance.
In conclusion, Polyaluminium Chloride plays a vital role in modern water treatment practices. Its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and lower environmental impact compared to traditional coagulants make it an invaluable asset in ensuring safe drinking water and managing wastewater. With the ongoing challenges of water pollution and scarcity, the continued exploration and utilization of PAC in water treatment are essential for sustainable water management practices in the future.
-
The Power of Isothiazolinones in Modern ApplicationsNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants in Water TreatmentNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants and Chemical Solutions: What You Need to KnowNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants and Chemical Solutions: A Growing IndustryNewsMay.08,2025
-
Essential Chemicals: Polymaleic Anhydride and MoreNewsMay.08,2025
-
Acrylic Polymers: Essential Solutions for IndustryNewsMay.08,2025





