Polyaluminum Chloride Applications in Effective Water Treatment Solutions for Improved Purity
Polyaluminum chloride (PAC) is a widely used coagulant in water treatment processes, particularly for drinking water and wastewater treatment. This chemical compound, which is a hydrolyzed form of aluminum chloride, plays a vital role in the removal of contaminants from water, making it essential for maintaining water quality and public health.
Polyaluminum chloride (PAC) is a widely used coagulant in water treatment processes, particularly for drinking water and wastewater treatment
. This chemical compound, which is a hydrolyzed form of aluminum chloride, plays a vital role in the removal of contaminants from water, making it essential for maintaining water quality and public health.The advantages of using PAC over traditional coagulants, such as alum (aluminum sulfate), are significant. PAC has a higher charge density, which allows it to effectively remove a broader range of contaminants at lower dosages. This efficiency not only reduces chemical costs but also minimizes the formation of residual sludge, leading to less waste to manage. Additionally, PAC improves the settling rates of flocs, resulting in shorter sedimentation times and enhancing the overall efficiency of the water treatment process.
polyaluminum chloride water treatment
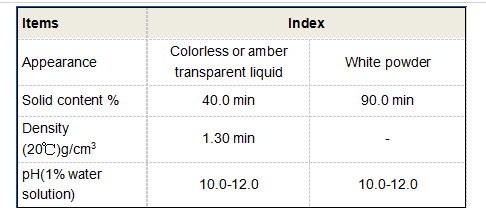
Furthermore, PAC is effective in dealing with a variety of water quality challenges, such as high turbidity and organic pollution. It can significantly improve the color and taste of water by removing organic compounds and color-causing compounds, ensuring that the treated water is aesthetically pleasing and meets drinking water standards. Its versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of water conditions, from surface water sources to industrial effluents.
The environmental impact of using PAC is also a noteworthy consideration. As PAC is produced through a more sustainable manufacturing process compared to other aluminum coagulants, its application in water treatment aligns with environmental protection goals. Furthermore, it has a lower ecological footprint, as its use generates less sludge, decreasing the burden on landfills and reducing the need for extensive sludge management systems.
In conclusion, polyaluminum chloride is an invaluable asset in modern water treatment practices. Its effectiveness in coagulating a wide range of contaminants, coupled with its efficiency and reduced environmental impact, makes PAC a preferred choice for water treatment facilities worldwide. As the global demand for clean and safe water continues to rise, the role of polyaluminum chloride in ensuring water quality will undoubtedly remain crucial in addressing public health and environmental challenges.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





