different types of flocculants
Different Types of Flocculants A Comprehensive Overview
Flocculants play a crucial role in various industrial and environmental applications, particularly in water treatment and sedimentation processes. These chemical substances facilitate the aggregation of fine particles into larger clusters or flocs, which can then be easily separated from liquid. Understanding the different types of flocculants can help in selecting the appropriate one for specific applications, optimizing processes, and ensuring environmental compliance.
1. Inorganic Flocculants
Inorganic flocculants are derived from mineral compounds and are widely used due to their effectiveness and cost efficiency. Some common types include
- Alum (Aluminum Sulfate) One of the most popular inorganic flocculants, alum works by neutralizing the charge on fine particles, allowing them to clump together. It is widely used in drinking water treatment, wastewater treatment, and paper manufacturing.
- Ferric Chloride This inorganic coagulant offers high efficiency in removing organic matter and phosphorus from wastewater. Ferric chloride can enhance the floc formation process by creating a larger particle mass, making sedimentation easier.
- Lime (Calcium Hydroxide) Lime is primarily used to adjust the pH of wastewater, but it can also act as a flocculant by promoting the coagulation of negatively charged particles. This method is particularly effective in treating industrial effluents.
2. Organic Flocculants
Organic flocculants are typically synthesized from natural or synthetic polymers and are known for their effectiveness in low-concentration suspensions.
- Natural Polymers These include substances derived from plant and animal sources, such as guar gum and starches. They are biodegradable and non-toxic, making them suitable for various applications, including food processing and environmental remediation.
- Synthetic Polymers Synthetic organic flocculants, like polyacrylamides, are tailored to specific applications through controlled polymerization processes. They can be non-ionic, anionic, or cationic, depending on their charge properties. Cationic flocculants are particularly effective for treating negatively charged particles, while anionic counterparts are ideal for positively charged particles.
different types of flocculants
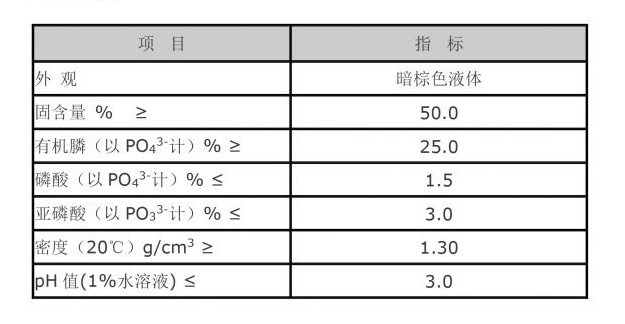
Bioflocculants are emerging as an eco-friendly alternative to conventional flocculants. Typically produced by microorganisms, these natural agents play a vital role in various environmental applications.
- Microbial Exopolysaccharides Certain bacteria and fungi produce exopolysaccharides, which have flocculating properties. These substances enhance sedimentation and aggregation of particles in wastewater treatment processes. Their biodegradability and low toxicity make them suitable for sustainable practices.
- Algal Flocculants Some microalgae produce flocculants that can be harvested for water treatment applications. These bioflocculants can effectively remove suspended solids and organic materials while promoting algal biomass growth for further uses, such as biodiesel production.
4. Application-Based Considerations
When selecting a flocculant, several factors should be considered to ensure optimal performance
- Nature of the Suspended Particles The size, charge, and type of particles present in the solution significantly influence the choice of flocculant. Understanding the physicochemical properties of the particles can help in selecting the most effective agent.
- Process Conditions Factors such as pH, temperature, and ionic strength of the solution can affect flocculation efficiency. It is crucial to match the flocculant characteristics with the specific conditions of the treatment process.
- Environmental Impact The sustainability and biodegradability of flocculants are becoming increasingly important, especially in industries aiming to reduce their environmental footprint. Choosing organic or bio-based flocculants can be a step towards more sustainable practices.
Conclusion
The choice of flocculant is integral to the efficiency of sedimentation and water treatment processes. Understanding the various types of flocculants, including inorganic, organic, and bioflocculants, allows for informed decisions that can enhance process efficiency while prioritizing environmental sustainability. As the demand for cleaner water increases, exploring innovative flocculant technologies will be key to meeting regulatory requirements and achieving sustainable industrial practices.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





