Cas 139-07-1 - Comprehensive Information on 2-Aminothiazole
Understanding CAS 139-07-1 The Significance of Chemical Substances in Industry
CAS 139-07-1 refers to the chemical compound known as 3,5-dimethylphenol, a member of the phenolic family. This compound, often utilized in industrial applications, showcases the pivotal role that specific chemical substances play in various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and materials science.
Chemical Structure and Properties
3,5-dimethylphenol is characterized by its aromatic ring structure, with two methyl groups located at the 3rd and 5th positions. This unique arrangement bestows specific chemical properties, including increased reactivity and oil solubility, making it a valuable intermediate in chemical synthesis. Its molecular formula, C8H10O, indicates the presence of an -OH (hydroxyl) group, typical of alcohols and phenols, which allows it to participate in a range of chemical reactions.
Understanding CAS 139-07-1 The Significance of Chemical Substances in Industry
In the industrial landscape, 3,5-dimethylphenol serves as a versatile building block for the synthesis of various compounds. One of its primary applications is in the production of antiseptics, where its bactericidal properties are harnessed. Additionally, this compound is used in the manufacturing of dyes and pigments, thanks to its ability to undergo diazotization and coupling reactions. Furthermore, its significance extends to the polymer industry, where it acts as a precursor to phenolic resins, which are widely employed in the fabrication of adhesives and coatings.
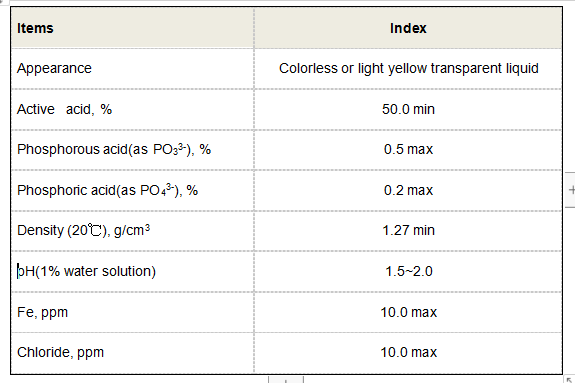
cas 139 07 1
Environmental and Health Considerations
Despite its utility, 3,5-dimethylphenol's usage is accompanied by health and environmental concerns. Exposure to this compound can pose risks, with potential effects on human health including skin irritation and respiratory issues. Therefore, industries utilizing this chemical must adhere to stringent regulations governing the handling and disposal of hazardous substances. Environmental monitoring is equally crucial to assess the impact of phenolic compounds on ecosystems and ensure compliance with safety standards.
Future Prospects
The demand for 3,5-dimethylphenol and similar compounds is anticipated to grow, driven by advances in material science and the need for efficient chemical processes. Ongoing research into sustainable synthesis methods, biocompatibility, and green chemistry principles may provide innovative pathways to enhance the utility of 3,5-dimethylphenol while mitigating its environmental impact.
Conclusion
In summary, CAS 139-07-1 exemplifies the intricate relationship between chemical substances and industrial applications. By understanding the properties, uses, and implications of 3,5-dimethylphenol, industries can maximize its potential while addressing the challenges associated with its use. Moving forward, a balanced approach that emphasizes safety and sustainability will be essential in harnessing the beneficial attributes of this and other chemical compounds.
-
The Power of Isothiazolinones in Modern ApplicationsNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants in Water TreatmentNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants and Chemical Solutions: What You Need to KnowNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants and Chemical Solutions: A Growing IndustryNewsMay.08,2025
-
Essential Chemicals: Polymaleic Anhydride and MoreNewsMay.08,2025
-
Acrylic Polymers: Essential Solutions for IndustryNewsMay.08,2025





