organophosphonates
Understanding Organophosphonates Structure, Uses, and Environmental Impact
Organophosphonates, a subclass of organophosphorus compounds, are characterized by their phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bonds. This unique structural feature distinguishes them from more commonly known organophosphates, which primarily consist of phosphorus-oxygen (P-O) bonds. The significance of organophosphonates has surged in recent years, thanks to their diverse applications and potential environmental impacts.
Structure and Properties
Organophosphonates generally consist of a phosphorus atom bonded to an organic residue, substituents, and carbon-containing groups, giving rise to a wide array of chemical properties. A notable example of this class is methylphosphonic acid (MPA), which is formed by the hydrolysis of certain organophosphonates and is a subject of study due to its relevance in both chemistry and environmental science.
The P-C bond present in organophosphonates is typically more stable than the P-O bond found in organophosphates. This stability contributes to the persistence of organophosphonates in the environment, leading to concerns over their potential accumulation and long-term effects.
Applications
One of the main applications of organophosphonates lies in agriculture, where they serve as effective herbicides and pesticides. Their ability to inhibit the activity of specific enzymes makes them highly effective in controlling unwanted plant growth and pests. This effectiveness has positioned them as valuable agents in modern agriculture, particularly as the agricultural industry seeks to enhance crop yields and sustainability.
Additionally, organophosphonates have found utility in the field of materials science
. They are used as flame retardants, plasticizers, and stabilizers in various polymer formulations. Their unique properties help enhance the fire resistance and thermal stability of materials, making them critical in the production of construction materials, textiles, and electronics.organophosphonates
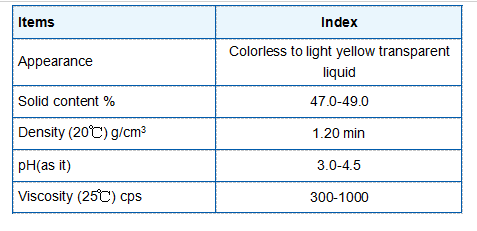
Moreover, organophosphonates play a significant role in water treatment processes. Due to their ability to sequester metal ions, they are employed to prevent scaling and corrosion in industrial systems. This application is vital in maintaining the operational efficiency of various industrial processes, reducing maintenance costs and extending the lifespan of equipment.
Environmental Concerns
Despite their useful applications, the environmental impact of organophosphonates cannot be overlooked. Their stability in the environment raises concerns about bioaccumulation and toxicity to non-target organisms. Laboratory studies indicate that some organophosphonates can be toxic to aquatic life; therefore, the release of these compounds into rivers and lakes must be managed carefully.
The persistence of organophosphonates in the environment can lead to long-term ecological damage. For instance, the degradation processes of these compounds are slower compared to other organophosphorus compounds, resulting in their accumulation in soil and water ecosystems. This aspect raises alarms regarding food chain contamination and the potential risks this poses to wildlife and human health.
Additionally, the use of organophosphonates in agriculture can lead to runoff during rain events, further spreading these compounds beyond their intended application zones. Mitigating measures, such as implementing best management practices and developing more biodegradable alternatives, are essential in combating the adverse environmental implications associated with their use.
Conclusion
In summary, organophosphonates represent a significant and multifaceted group of compounds that hold considerable promise in agriculture, materials science, and water treatment. However, their environmental persistence and potential toxicity underscore the need for careful monitoring and regulation. Ongoing research is vital to fully understand their behavior in ecosystems and to develop safer alternatives that can minimize the ecological footprint associated with their use.
The balance between leveraging the benefits of organophosphonates and mitigating their environmental impacts is critical for achieving sustainable development in various sectors. By fostering innovation in this field and promoting responsible usage, we can ensure that organophosphonates contribute positively while protecting our environment for future generations.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





