polyaluminum chloride coagulant
The Role of Polyaluminum Chloride as a Coagulant
Polyaluminum chloride (PAC) is a widely used coagulant in water treatment processes. Its popularity stems from its effectiveness in removing suspended solids, organic matter, and other impurities from water. This article will explore the properties, benefits, and applications of PAC, as well as its environmental implications.
Understanding Polyaluminum Chloride
Polyaluminum chloride is a chemical compound that is composed of aluminum, chlorine, and hydroxide. It is produced through the hydrolysis of aluminum chloride in water, resulting in a polymeric form that is more efficient for coagulation than traditional aluminum sulfate (alum). PAC can vary in its composition and can be found in both liquid and dry forms. The chemical formula can be represented as Aln(OH)mCl(3n-m), where different n and m values create variations designed for specific water treatment needs.
Benefits of Using Polyaluminum Chloride
One of the primary advantages of PAC is its increased efficiency compared to traditional coagulants. PAC can effectively destabilize colloids and aggregate particles at lower doses due to its higher charge density. This property allows for better floc formation, facilitating the sedimentation process and enhancing the removal of impurities.
Another benefit of using PAC is its broad pH operational range. PAC performs effectively in a variety of pH levels, making it suitable for different types of water sources. It is also less sensitive to water temperature changes, maintaining its coagulant performance even in colder conditions. This versatility makes PAC a preferred choice for municipal water treatment facilities, industrial applications, and wastewater treatment plants.
Moreover, PAC generally produces fewer residuals than traditional aluminum salts, which can be particularly beneficial in drinking water treatment
. The lower levels of residual aluminum can lead to reduced health concerns and regulatory compliance issues concerning aluminum in potable water.Applications in Water Treatment
polyaluminum chloride coagulant
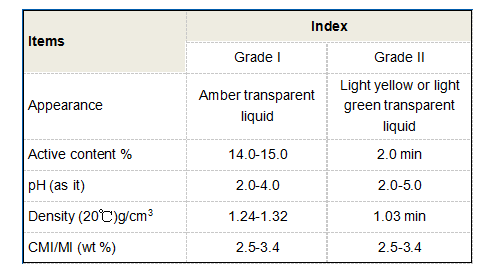
Polyaluminum chloride is utilized in a variety of water treatment applications, including potable water purification, wastewater treatment, and industrial processes. In municipal systems, PAC is employed to treat drinking water, effectively removing turbidity, algae, and pathogens, ensuring safe and clean water for consumption.
In wastewater treatment, PAC is used to enhance the removal of suspended solids and phosphorus, contributing to the overall efficiency of the treatment process. Its effectiveness in dewatering sludge makes it an attractive option in both municipal and industrial wastewater facilities, improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Moreover, PAC has found applications in the paper and pulp industry, where it is used as a coagulant in the paper manufacturing process. It aids in the retention of fibers and fillers, contributing to improved paper quality while minimizing waste.
Environmental Considerations
While PAC offers several advantages, it is essential to consider its environmental impact. PAC can release aluminum ions into treated water, which, in high concentrations, may pose risks to aquatic life and human health. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor the dosage and residual levels in treated water to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Sustainable practices and advances in formulation are also being explored to minimize any negative effects associated with PAC use. This includes the development of optimized polyelectrolytes that can offer similar benefits with reduced environmental footprints.
Conclusion
Polyaluminum chloride is a vital coagulant in modern water treatment processes, providing effective solutions for various applications. Its advantages over traditional coagulants make it an essential component in ensuring the purity and safety of water supplies. However, as with all chemical applications, it is imperative to use PAC responsibly and monitor its environmental impact to safeguard public health and the ecosystem. Through ongoing research and regulation, PAC can continue to serve the critical role of water purification while aligning with sustainability goals.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





