2 phosphonobutane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
Exploring Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid and Its Applications
Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTC) is a chemical compound that has garnered attention due to its versatile applications across various industries. As a phosphonic acid derivative, PBTC combines both carboxylic functional groups and phosphonic acid features, providing unique properties that make it suitable for several industrial applications, particularly in water treatment and scale inhibition.
Chemical Structure and Properties
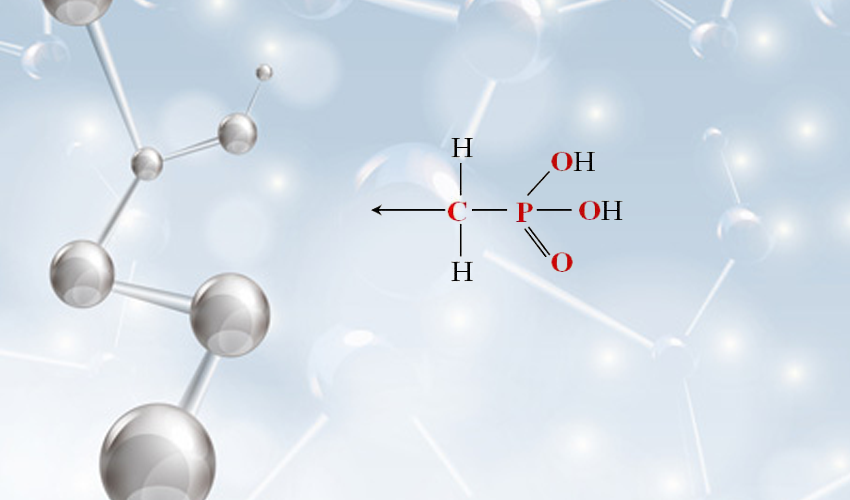
PBTC is characterized by its molecular structure, which includes a butane backbone with three carboxylic acid groups and one phosphonic acid group. This structure imparts a high degree of polarity to the molecule, enhancing its solubility in aqueous environments. The presence of phosphonic acid groups contributes to its chelating abilities, allowing it to bind effectively with metal ions. This property is particularly beneficial in water treatment applications where it functions to prevent scale formation by sequestering calcium, magnesium, and other metal ions that can lead to deposits.
Applications in Water Treatment
One of the primary applications of PBTC is in water treatment, particularly in cooling water systems. In industrial settings, such as power plants and chemical manufacturing facilities, water is often recirculated to save resources. However, this practice can lead to the accumulation of scale and corrosion, which not only reduces the efficiency of the systems but also increases maintenance costs. PBTC acts as an excellent scale inhibitor, reducing the likelihood of deposits forming on equipment. By keeping dissolved calcium and other minerals in solution, PBTC helps maintain the efficiency of these systems and minimizes downtime due to maintenance.
Benefits over Other Scale Inhibitors
2 phosphonobutane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
PBTC has several advantages compared to traditional scale inhibitors. Its exceptional stability and performance in a wide range of pH levels make it particularly advantageous in varying water chemistry conditions. While some scale inhibitors may break down or lose effectiveness under certain conditions, PBTC retains its chelating abilities. Additionally, it is less prone to hydrolysis and has a lower toxicity profile compared to other organic phosphonates, making it a more environmentally friendly choice for water treatment.
Use in Agriculture
Beyond industrial applications, PBTC is also making waves in agriculture, particularly in fertilizers and soil conditioners. The chelating properties of PBTC allow it to bind with essential nutrients, aiding in their absorption by plants. This is especially beneficial in calcareous soils where nutrients may become locked in forms that are unavailable to plants. By utilizing PBTC in fertilizers, farmers can enhance nutrient uptake, leading to improved crop yields and overall plant health.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is exploring the broader applications of PBTC in sectors such as oil and gas, personal care products, and food processing. Its potential as a corrosion inhibitor is being investigated, as industries seek effective methods to protect equipment from deterioration. Moreover, with the growing emphasis on sustainability, PBTC’s biodegradability and lower environmental impact position it well in a market that increasingly values green chemistry principles.
Conclusion
Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid represents an essential compound in modern industrial applications, particularly in water treatment and agriculture. Its unique chemical properties offer significant advantages in scale inhibition, nutrient absorption, and environmental safety. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and efficiency, PBTC is likely to become a focal point of research and utilization across multiple sectors. With its versatility and effectiveness, PBTC not only addresses current industrial challenges but also paves the way for innovative solutions that align with environmentally responsible practices.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





