Synthesis and Characterization of 2% Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid for Biochemical Applications
The Significance of 2% Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic Acid in Modern Chemistry
Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTC) has garnered significant attention in various fields of chemistry and industry due to its unique properties and applications. As a phosphonic acid derivative with multiple carboxylic groups, PBTC plays a crucial role as a chelating agent, making it an invaluable compound in both academic research and industrial practices.
First synthesized in the mid-20th century, PBTC is structured with a butane backbone and three carboxylic acid groups, along with a phosphonic acid group. This configuration allows PBTC to effectively bind to metal ions, which is fundamental in numerous applications, including water treatment, detergents, and agricultural chemicals. Its ability to form stable complexes with metals makes it an essential component in controlling scaling and corrosion in water systems.
The Significance of 2% Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic Acid in Modern Chemistry
Furthermore, PBTC has been recognized for its role in the agricultural sector, particularly as a component in fertilizers and plant protection products. Its chelating properties allow it to enhance the solubility of essential micronutrients, ensuring better nutrient uptake by plants. By facilitating the availability of nutrients such as iron, zinc, and manganese, PBTC contributes to improved crop yields and overall plant health. This is particularly crucial in regions with nutrient-deficient soils, where the use of PBTC can significantly enhance agricultural productivity.
2 phosphonobutane 1 2 4 tricarboxylic acid
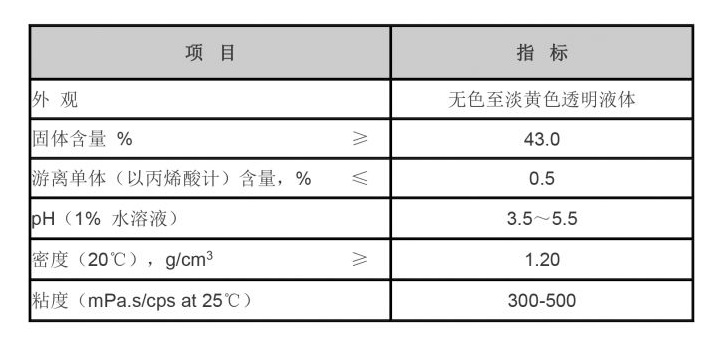
In addition to its applications in water treatment and agriculture, PBTC also finds utility in the formulation of cleaning agents and detergents. The compound's ability to disperse and sequester metal ions makes it effective in preventing staining and maintaining the clarity of cleaning formulations. As consumers increasingly demand eco-friendly and efficient cleaning products, PBTC serves as an attractive option due to its biodegradable nature and lower environmental impact compared to traditional phosphates.
Moreover, the versatility of PBTC is further underscored by its potential in the field of pharmaceuticals. Research is ongoing to explore its capabilities as a drug delivery system and its role in biomedical applications. The unique interaction of PBTC with biological systems may lead to innovative therapeutic strategies and advancements in drug formulations.
Despite its benefits, the use of PBTC and similar phosphonic acids warrants careful consideration regarding their environmental impact. While PBTC is generally regarded as safer than phosphates, ongoing research continues to assess its biodegradability and long-term effects on ecosystems. This highlights the importance of responsible usage and regulatory oversight to ensure that the advancements in chemistry align with sustainable practices.
In conclusion, 2% Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid represents a remarkable compound with broad implications across various sectors. From water treatment and agricultural enhancements to its potential in pharmaceutical applications, PBTC demonstrates the significant role chelating agents play in modern chemistry. As research progresses, the continued exploration of PBTC's applications will likely yield new insights and advancements, further establishing its importance in both industrial and scientific domains.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





