different types of flocculants
Understanding Different Types of Flocculants A Comprehensive Overview
Flocculants are essential chemicals used in various industries, particularly in water treatment and mineral processing. They play a crucial role in the aggregation of suspended particles, facilitating their removal through processes such as sedimentation or filtration. The effectiveness of flocculants can significantly impact the efficiency of treatment plants, making it vital to understand the different types available. This article explores the various categories of flocculants, their mechanisms, applications, and environmental considerations.
Types of Flocculants
Flocculants can be broadly classified into two categories organic and inorganic flocculants. Each category consists of several subtypes that cater to specific applications and operational conditions.
1. Organic Flocculants
Organic flocculants are synthesized from natural or synthetic organic polymers and are widely used due to their effectiveness and versatility. They are typically divided into four groups
- Natural Polymers These include starch, guar gum, and chitosan, which are derived from natural sources. They are biodegradable and less harmful to the environment, making them suitable for wastewater treatment in sensitive ecosystems.
- Synthetic Polymers Common synthetic organic flocculants include polyacrylamide (PAM) and its derivatives. PAM is widely used in industrial applications due to its high efficacy in binding particles. However, its environmental impact, particularly concerning residual toxicity, is a factor that must be managed.
- Cationic Flocculants These flocculants carry a positive charge and are particularly effective at neutralizing negatively charged particles in suspension. They are commonly used in municipal wastewater treatment and paper manufacturing.
- Anionic Flocculants These have a negative charge and are effective in higher pH conditions. Anionic flocculants are often employed in the treatment of effluents from mines and quarries.
2. Inorganic Flocculants
Inorganic flocculants are compounds comprised of metal salts that help in coagulation processes by neutralizing the charges on suspended particles. The most common inorganic flocculants include
- Alum (Aluminum Sulfate) One of the most widely used flocculants in water treatment, alum effectively aids in the removal of turbidity. It works by forming aluminum hydroxide, which traps suspended particles.
different types of flocculants
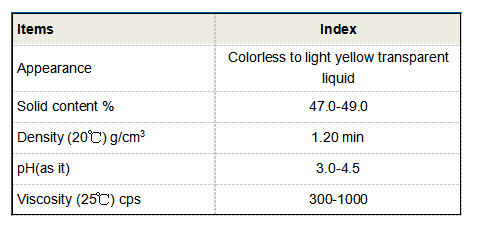
- Ferric Chloride and Ferric Sulfate These are iron-based flocculants that are particularly effective in treating wastewater with high organic content. They can remove phosphates effectively, thus preventing eutrophication in receiving waters.
- Calcium Hydroxide Often used to adjust pH levels in water treatment, calcium hydroxide can also function as a flocculant under certain conditions, particularly in lime softening processes
.Applications of Flocculants
Flocculants are prevalent in numerous applications
- Water Treatment They are primarily used to clarify drinking water and treat wastewater, enabling the removal of solids and pathogens.
- Mining and Mineral Processing Flocculants assist in the separation of valuable minerals from ore by promoting sedimentation and concentration of minerals.
- Pulp and Paper Industry In this sector, flocculants help in the dewatering process, allowing for enhanced recovery of fiber.
- Food Processing They are employed to clarify fruit juices and wine, enhancing the quality and stability of these products.
Environmental Considerations
While flocculants play a pivotal role in treatment processes, their use raises environmental concerns. Synthetic flocculants, especially polyacrylamide, can be hazardous to aquatic life if not properly managed. Therefore, the selection of appropriate flocculants should consider biodegradability, toxicity, and the overall environmental impact.
Moreover, advancements in research are focusing on the development of eco-friendly alternatives, such as biopolymers, which could provide similar performance with reduced ecological footprints.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of flocculants and their applications is crucial for optimizing processes in water treatment, mining, and other industries. By carefully selecting the appropriate flocculants, industries can enhance efficiency while minimizing environmental impacts. Future advancements will likely lead to even more sustainable flocculation solutions, balancing industrial needs with ecological responsibility.
-
LK-319 Special Scale And Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Plants: Advanced Solutions for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: Essential Chemical Solutions for Purification ProcessesNewsAug.22,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: Versatile Microbial Control Agents for Industrial and Consumer ApplicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor: Key Solutions for Water System Scale PreventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
Organophosphonates: Versatile Scale Inhibitors for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitor: Essential Chemical Solutions for Water System MaintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





