Exploring the Properties and Applications of HEDP Acid in Various Industries
Understanding HEDP Acid Its Properties, Applications, and Importance
HEDP, or Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid, is a powerful and versatile compound widely utilized in various industries due to its exceptional chelating properties. As a member of the phosphonate family, HEDP plays a crucial role in preventing scale formation and corrosion in water treatment processes. This article delves into the properties, applications, and significance of HEDP acid across different sectors.
Chemical Properties
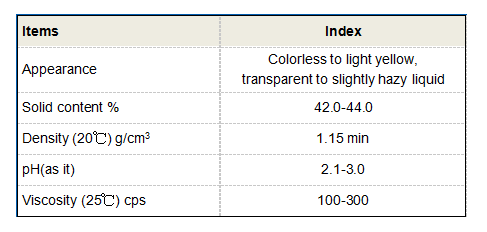
HEDP is a colorless to pale yellow liquid that is hygroscopic in nature. Its chemical formula is C2H8O7P2, which reflects its complex structure, consisting of two phosphonate groups linked to a hydroxyethylidene moiety. This unique composition enables HEDP to effectively bind metal ions such as calcium, magnesium, and iron, which are often responsible for scaling and fouling in water systems. With a high stability constant, HEDP forms stable complexes with these metal ions, rendering them inactive and preventing precipitation.
Applications in Water Treatment
One of the primary applications of HEDP is in water treatment processes, especially in cooling water systems, boilers, and oilfield operations. Water systems are prone to scaling and corrosion due to the presence of dissolved minerals and gases. HEDP acts as a scale inhibitor, preventing the formation of hard deposits that can impede water flow and efficiency.
In cooling towers, for instance, the accumulation of calcium carbonate can significantly reduce heat exchange efficiency. By incorporating HEDP into the water treatment regime, industries can minimize scaling and maintain optimal operational efficiency. Furthermore, HEDP’s ability to inhibit corrosion extends the lifespan of equipment, thereby reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
Use in Detergents and Cleaning Agents
hedp acid
HEDP is also a highly regarded ingredient in various cleaning products and detergents. Its chelating properties allow it to dissolve hard water minerals, which can effectively enhance the cleaning power of these formulations. When HEDP is included in laundry detergents or dishwashing liquids, it helps to improve the performance of surfactants, ensuring that dirt and stains are removed more effectively.
Additionally, HEDP finds applications in household cleaning products due to its ability to complex metal ions that can cause discoloration and diminish the efficacy of cleaning agents. This results in cleaner surfaces and improved overall effectiveness of the products.
Role in Agriculture
In agriculture, HEDP is used as a fertilizer additive. The chelating capabilities of HEDP enable it to bind essential micronutrients, making them more bioavailable to plants. This is particularly beneficial in regions with alkaline soils, where certain nutrients can be rendered insoluble. By improving nutrient availability, HEDP contributes to enhanced crop yield and overall agricultural productivity.
Environmental Considerations
While HEDP is highly effective in various applications, its environmental impact is also a topic of discussion. As with many chemical compounds, improper use or excessive discharge into water systems can lead to ecological imbalances. Therefore, it is crucial for industries utilizing HEDP to follow proper guidelines and regulations to mitigate any potential environmental hazards. Research continues into developing biodegradable alternatives that maintain the efficacy of HEDP while reducing environmental persistence.
Conclusion
HEDP acid is a significant compound in modern industrial applications, particularly in water treatment, cleaning products, and agriculture. Its outstanding chelating properties prevent scaling and corrosion, enhance the effectiveness of detergents, and improve nutrient availability in soils. However, responsible use and disposal are essential to ensure that its benefits do not come at the cost of environmental health. As industries continue to evolve, the role of HEDP will likely expand, highlighting the need for ongoing research and sustainable practices.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





