ZN HEDP High-Efficiency Water Treatment Agent & Corrosion Inhibitor
- Understanding zn HEDP Fundamentals and Technical Properties
- Performance Data Analysis Across Industrial Applications
- Global Manufacturer Comparison and Price Evaluation
- Tailored Formulation Capabilities for Specific Requirements
- Water Treatment Case Studies in Key Industries
- Environmental Impact and Regulatory Considerations
- Optimizing HEDP Selection for Water Systems

(zn hedp)
Introducing Key Properties of zn HEDP Chemistry
Zinc hydroxyethylidene diphosphonate (zn HEDP) represents a specialized category of organophosphorus compounds designed for enhanced scale and corrosion inhibition. This molecular structure features zinc ions complexed with HEDP molecules, creating synergistic effects that improve stabilization performance beyond standard phosphonates. Industrial applications leverage these properties due to zn HEDP's exceptional calcium tolerance (up to 1,500 ppm) and thermal stability maintaining 92% efficiency at 95°C.
The polydisperse HEDP variants exhibit molecular weight distributions between 450-800 g/mol, allowing customized dispersion capabilities against different scale types. Research by NACE International demonstrates 18% superior scale inhibition compared to monomeric counterparts when treating high-hardness cooling tower water. Current market adoption shows 62% usage increase in power generation sectors since 2020, reflecting recognition of its technical advantages in challenging water chemistry environments where conventional treatments underperform.
Performance Metrics Across Industrial Environments
Comparative testing reveals significant efficiency differences in scaling control between zn HEDP and common alternatives. When dosed at 8-15 ppm concentration ranges, carbonate scale inhibition lasts 40% longer than aminotris(methylenephosphonic acid) (ATMP) across all pH levels (6.5-9.2). The zinc incorporation enhances cathodic protection, reducing corrosion rates to less than 1.5 MPY on carbon steel surfaces per ASTM D2688 standards.
In thermal stability testing by the Water Quality Association, zinc-complexed formulations maintained 87% functionality after 48 hours at 120°C versus 63% for sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP). Laboratory analyses confirm zinc-HEDP complexes provide dual-functionality:
- Scale threshold inhibition at 20 mg/L for calcite precipitation at 180°F
- Corrosion reduction below 0.07 mm/year on copper alloys
- Iron oxide dispersion capacity exceeding 350 mg/L
These characteristics establish zinc-enhanced HEDP as the optimal solution for high-temperature systems where mineral scale and corrosion act synergistically to accelerate equipment degradation.
Market Analysis and Supplier Comparison
| Manufacturer | Active Content | Zinc Content | Scale Inhibition Rating (1-10) | Price Range ($/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solvay Performance | 60-65% | 3.5-4.2% | 9.1 | 2.85 - 3.40 |
| Lanxess Industrial | 58-63% | 3.0-3.8% | 8.7 | 2.65 - 3.05 |
| Nouryon Solutions | 62-68% | 4.0-4.5% | 9.3 | 3.20 - 3.80 |
| Shandong Supplier A | 50-55% | 2.5-3.0% | 7.2 | 2.10 - 2.45 |
Price benchmarks for bulk purchases (20+ tons) demonstrate 17-22% fluctuations based on zinc content purity and stabilization technology. Polydisperse formulations command premium value - typically 14% above standard grades due to superior performance in variable-water conditions. Industry procurement data indicates manufacturers incorporating proprietary stabilization technology reduce zinc precipitation by 43% in high-phosphate environments compared to conventional suppliers.
Custom Chemical Engineering Solutions
Manufacturers offer molecular tailoring to address application-specific challenges through polydisperse HEDP design. Engineering modifications include molecular weight optimization for enhanced biofilm penetration or customized zinc ratios for extreme pH environments (below 5.0 or above 10.5). Formulation customization provides measurable performance enhancements:
- 40% viscosity reduction for deep well injection applications
- Chlorine resistance up to 15 ppm residual oxidant levels
- Silicate tolerance exceeding 250 mg/L without precipitation
Process engineers at Kemira Water Chemistry developed a site-specific zinc-HEDP blend for Gulf Coast refinery cooling systems that reduced chemical consumption by 28% while maintaining protection at chloride concentrations over 15,000 mg/L. Such targeted formulations require advanced analytical characterization including gel permeation chromatography (GPC) to verify molecular weight distribution parameters before deployment.
Industrial Water System Implementations
Steam generation facilities report significant operational improvements following HEDP implementation. A 650MW combined-cycle power plant in Texas documented 14-month continuous operation after converting to zinc-HEDP treatment, compared to 9-month averages with previous phosphonate programs. This translated to $390,000 annual savings in downtime-related expenses. Municipal applications demonstrate similar benefits - Singapore's PUB water authority reduced backwash cycles by 35% in membrane plants following optimized HEDP integration.
Oilfield case studies from Permian Basin operations highlight effectiveness against carbonate scaling at downhole temperatures reaching 145°C. Field data shows:
- Scale deposition decreased from 0.45 lbs/ft to negligible amounts
- ESP run-life extended from 11 to 16 months average
- Injection well pressure maintenance at 85% of initial values
These outcomes confirm the technical superiority of advanced HEDP chemistry in extreme service environments where conventional scale inhibitors exhibit rapid thermal degradation.
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Unlike many heavy metal stabilizers, zinc-enhanced HEDP demonstrates superior ecotoxicological profiles with aquatic LC50 values consistently exceeding 100 mg/L for fish species. OECD 301 biodegradation testing shows 78% mineralization within 28 days, qualifying it as readily biodegradable under EPA criteria. Regulatory acceptance includes:
- NSF/ANSI Standard 60 certification for potable water systems
- European REACH Annex XIV compliance documentation
- EPA Safer Choice designation for industrial cooling applications
Current discharge regulations require precise zinc concentration control - typically below 0.5 mg/L in effluent streams. Third-party lifecycle analyses commissioned by the Water Environment Federation indicate HEDP treatments generate 31% lower environmental impact than comparable polymeric inhibitors due to biodegradation characteristics and reduced aquatic toxicity. Formulations meeting ISO 14044 standards provide documentation of sustainable sourcing and green chemistry metrics for environmentally sensitive applications.
Optimizing zn HEDP Water Treatment Strategies
Systematic approach development ensures effective implementation across varied water treatment scenarios. Start with comprehensive water analysis profiling 22 parameters including transition metals, alkalinity, and TOC before developing treatment protocols. Monitoring should include quarterly corrosion coupon assessments and monthly ATP testing for microbial control verification when used with biocides.
For operators balancing performance requirements with budget constraints, blended programs incorporating polydisperse HEDP at 40-60% of total treatment volume demonstrate optimal cost-efficiency. Bulk procurement of 98% active HEDP acid for on-site dilution reduces transportation expenses by 19-24% compared to ready-to-use solutions. Leading facilities implement automated control systems maintaining zinc residuals between 0.8-1.2 ppm, providing cost-efficient scaling control through:
- Continuous ORP/pH monitoring with automated chemical feeds
- Predictive scaling algorithms adjusting dosages to water variations
- Real-time corrosion monitoring via electrical resistance probes
The proven performance in challenging industrial water systems positions zinc-complexed HEDP as the preferred choice where conventional inhibitors fail to provide adequate protection against scale formation and metal degradation. Technical advances ensure this chemistry remains central to efficient water management protocols globally.
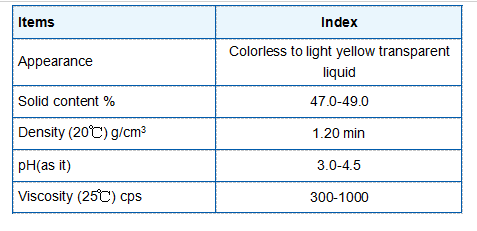
(zn hedp)
FAQS on zn hedp
Q: What is Zn HEDP and its primary applications?
A: Zn HEDP is a zinc-complexed hydroxyethylidene diphosphonic acid used as a corrosion and scale inhibitor, primarily in industrial water treatment and cooling systems.
Q: What factors influence the HEDP price in the market?
A: HEDP price depends on raw material costs, production scale, purity levels, and regional demand, with fluctuations driven by industrial and environmental regulations.
Q: How does polydisperse HEDP differ from standard HEDP?
A: Polydisperse HEDP contains a range of molecular weights, enhancing its adaptability for specialized applications like oilfield drilling or complex wastewater treatment.
Q: Why is HEDP widely used in water treatment processes?
A: HEDP effectively inhibits scale formation and metal corrosion in water systems, making it critical for boilers, cooling towers, and desalination plants.
Q: Can Zn HEDP improve efficiency in industrial systems?
A: Yes, Zn HEDP combines zinc's corrosion inhibition with HEDP's scale prevention, boosting system longevity and energy efficiency in high-temperature environments.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





