hedp in soap
The Role of HEDP in Soap Production
HEDP, or Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid, is a versatile compound that has found applications in various industries, including detergents and personal care products. Its unique chemical properties make it a valuable additive in soap production, enhancing the effectiveness and quality of the final product.
The Role of HEDP in Soap Production
Aside from its chelating abilities, HEDP is also known for its low toxicity and environmental friendliness. As consumers become more aware of the impact of their purchases on the planet, the demand for eco-friendly products has surged. HEDP is biodegradable under certain conditions, making it a suitable choice for manufacturers looking to create sustainable products. This aligns well with the growing trend of green chemistry in the cosmetics industry, where minimizing harmful substances and maximizing eco-safety are of paramount importance.
hedp in soap
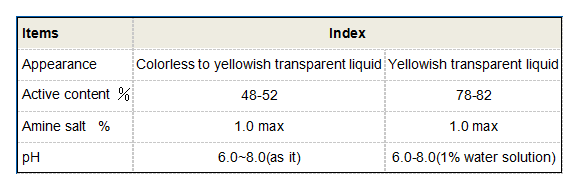
Moreover, HEDP can enhance the stability and shelf-life of soap formulations. Its ability to inhibit the formation of scale due to precipitated hardness ions also means that products containing HEDP are less likely to suffer from product degradation over time. The inclusion of HEDP can lead to a more consistent user experience, yielding a product that performs reliably across its shelf life.
Another key advantage of HEDP in soap production is its effectiveness in low concentrations. This means that manufacturers can achieve the desired effect without overusing the chemical, which is a significant consideration in product formulation. Efficient use of HEDP helps in managing costs while ensuring high-quality outcomes in the final product.
In conclusion, the inclusion of HEDP in soap production serves multiple essential functions, from enhancing cleaning efficiency to ensuring product stability. Its role as a chelating agent addresses common challenges posed by hard water, while its environmentally friendly profile aligns well with contemporary consumer preferences. As the soap industry continues to evolve, the importance of such additives will likely grow, highlighting the need for continued innovation and adaptation in formulation strategies.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





