Exploring the Role of Flocculation in Enhancing Water Purification Processes and Techniques
Flocculation in Water Purification
Water purification is a critical process that ensures the availability of clean and safe drinking water. Among the various methods employed in this process, flocculation stands out as a key technique for removing suspended particles and colloids, thus improving the quality of water. This article delves into the principles of flocculation, its process, and its significance in water treatment.
Flocculation is the process where fine particulates are agglomerated into a floc, or clump, which can then be easily separated from water. It typically follows a coagulation step, where chemical coagulants are added to destabilize the suspended particles. Common coagulants include aluminum sulfate, ferric chloride, and polymeric substances. These coagulants neutralize the charges that keep the particles suspended, allowing them to bind together and form larger aggregates known as flocs.
Flocculation in Water Purification
The efficiency of flocculation is influenced by several factors, including pH, temperature, and the concentration of coagulants. For instance, the pH of the water needs to be optimal for the coagulation process, as it affects the solubility and charge of the coagulants. Operating within the right pH range enhances coagulation effectiveness, leading to better floc formation and removal rates.
flocculation in water purification
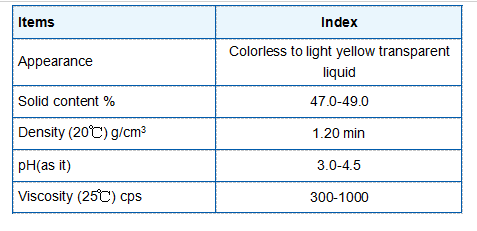
One of the significant advantages of flocculation is its ability to remove not only particulate matter but also microorganisms and other contaminants. By effectively aggregating particles, flocculation can reduce turbidity, which is a measure of how clear the water is. High turbidity levels often indicate the presence of pathogens that pose health risks. Thus, by lowering turbidity, flocculation contributes to the microbiological safety of drinking water.
Flocculation also plays a vital role in other aspects of water treatment, including the removal of excess nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, which can lead to algal blooms in water bodies. These blooms not only reduce water quality but also disrupt aquatic ecosystems. Therefore, incorporating flocculation into water treatment processes aids in the prevention of these ecological issues.
Moreover, flocculation is beneficial in wastewater treatment, where it helps remove pollutants before the water is discharged into the environment. The treated water can then be reused or returned to natural water bodies, promoting sustainability and reducing the impact on aquatic ecosystems.
In conclusion, flocculation is an essential process in water purification that enhances the removal of suspended particles, pathogens, and other contaminants. By converting fine particles into larger, manageable aggregates, it facilitates the efficient separation and treatment of water. As water scarcity becomes an increasing global concern, mastering flocculation processes will be crucial for ensuring the delivery of safe, clean drinking water and protecting environmental integrity. Through continued advancements and optimization of flocculation methods, water treatment facilities can improve their operational efficiency and contribute to a healthier planet.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





