flocculant types
Understanding Flocculant Types and Their Applications
Flocculants are crucial agents used in various industrial processes to promote the agglomeration of fine particles into a floc or a larger mass. This process, known as flocculation, is essential in a myriad of applications, including water treatment, mineral processing, and food production. Understanding the different types of flocculants available can help industries select the most appropriate agents for their specific needs.
1. Natural Flocculants
Natural flocculants are derived from organic sources, including plant extracts and microbial substances. Common examples include starches, guar gum, and alginates, which are favored for their eco-friendliness and biodegradability. Natural flocculants operate effectively in neutral to slightly alkaline conditions and are often used in applications like wastewater treatment, where they can assist in clarifying water while posing minimal environmental risks.
Natural flocculants can be particularly beneficial in situations where chemical residues might be undesirable. For example, in the food industry, products derived from natural sources are preferred for applications such as juice clarification and beer brewing, where taste and safety are paramount.
Synthetic flocculants are manufactured through chemical processes and offer customized properties tailored to specific applications. They typically come in two forms anionic and cationic. Anionic flocculants have a negative charge and are effective in removing positively charged particles. Conversely, cationic flocculants possess a positive charge, making them suitable for treating negatively charged particles.
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is one of the most widely used synthetic flocculants. Its versatility allows it to be utilized in various fields, from municipal wastewater treatment to mining operations. Each synthetic flocculant type provides distinct performance advantages, making it essential to match the flocculant type with the particle charge and the process conditions to achieve optimal results.
flocculant types
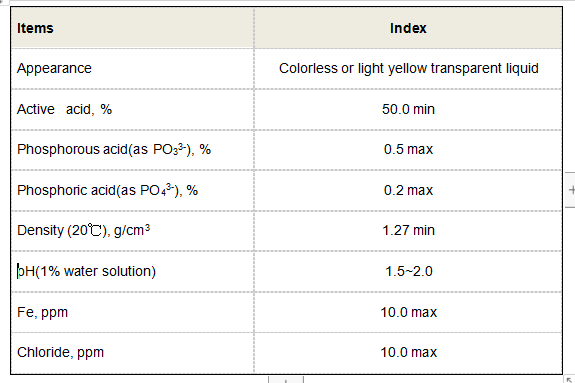
3. Inorganic Flocculants
Inorganic flocculants, such as aluminum sulfate (alum) and ferric chloride, are commonly used in water treatment processes. These agents function by coagulating impurities in the water, forming larger aggregates that can be easily removed. Inorganic flocculants tend to work well in acidic to neutral pH conditions, making them a popular choice for municipal water treatment plants.
The use of inorganic flocculants in industrial applications often hinges on their effectiveness and cost-efficiency. However, one must also consider potential residuals and sludge production, making the disposal and treatment of by-products a critical part of the overall process.
4. Biopolymers and Emerging Alternatives
Recent developments in flocculant technology have introduced biopolymers and other innovative materials as alternative flocculants. These include chitosan, derived from crustacean shells, and other biodegradable polymers that demonstrate effective flocculation capabilities while minimizing ecological impacts. The growing trend towards sustainability drives research into these bio-based alternatives as industries seek to reduce their carbon footprint.
Conclusion
The choice of flocculant type—natural, synthetic, inorganic, or emerging alternatives—depends on various factors, including cost, efficiency, environmental impact, and specific operational conditions. As industries continue to evolve towards greener practices, the development and adoption of sustainable flocculants will play a vital role in ensuring effective particle agglomeration while fostering environmental responsibility. Understanding these types of flocculants and their respective applications is essential for optimizing industrial processes and achieving better outcomes in both production efficiency and environmental stewardship.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





