Exploring the Effects of Poly Aluminium Chloride on pH Levels in Water Treatment Applications
Polyaluminium Chloride (PAC) and its pH Understanding the Importance in Water Treatment
Polyaluminium chloride (PAC) has emerged as a crucial coagulant widely utilized in water treatment processes. It is a polymeric aluminum inorganic coagulant that facilitates the removal of suspended particles, colloids, and impurities in water. One of the vital characteristics of PAC that significantly influences its effectiveness is its pH level. Understanding the relationship between PAC and pH can enhance water treatment operations and improve the overall quality of treated water.
PAC is favored over traditional coagulants, like aluminum sulfate, due to its enhanced performance across a broader range of pH levels. Typically, PAC solutions exhibit a pH range between 3.5 and 5.0, which can vary depending on the formulation and the specific application. The efficacy of PAC as a coagulant is largely contingent upon its pH during the treatment process. The pH directly affects the charge and availability of aluminum species, which play a pivotal role in the coagulation and flocculation processes.
Polyaluminium Chloride (PAC) and its pH Understanding the Importance in Water Treatment
Conversely, as the pH increases, the solubility of aluminum hydroxides rises, leading to the formation of larger, less effective flocs. If the pH surpasses the optimum range for PAC application, the performance of the coagulant diminishes, leading to inadequate particle removal and a decline in water quality. This underscores the necessity for careful pH monitoring and adjustment during water treatment processes that utilize PAC.
polyaluminium chloride ph
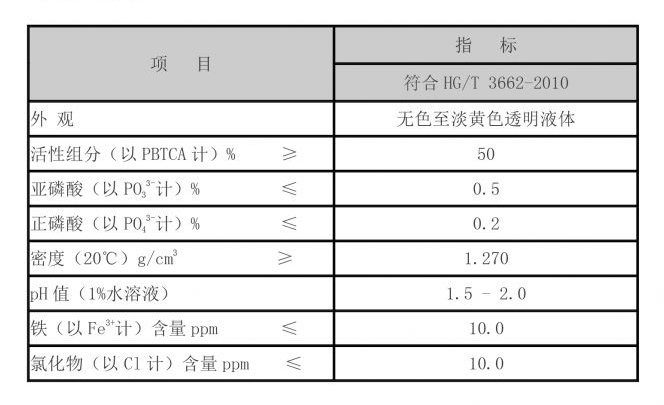
In practical applications, operators often aim for a water treatment pH between 6.5 and 8.5 to optimize the coagulation process. During this pH range, PAC tends to perform effectively in removing turbidity and dissolved organic matter. It is imperative for operators to conduct routine monitoring of the water pH and adjust it as necessary, particularly in surface water treatment where natural fluctuations can occur due to varying environmental conditions.
In addition to enhancing coagulation, appropriate pH levels can also minimize potential health risks associated with aluminum exposure in drinking water. Excessive aluminum can lead to adverse health effects, making it essential to adhere to regulatory standards regarding aluminum residues in treated water. By optimizing the pH levels during pac applications, water treatment facilities can significantly reduce aluminum concentrations, ensuring the safety and quality of the treated water supplied to consumers.
Furthermore, understanding the impact of pH on PAC usage can also lead to cost efficiencies in water treatment operations. By maintaining the correct pH, water treatment facilities can minimize the required dosage of PAC, thereby reducing operational costs and improving treatment performance. This not only enhances the sustainability of water treatment processes but also contributes to better resource management.
In conclusion, the pH level plays a pivotal role in the performance of polyaluminium chloride as a coagulant in water treatment. By closely monitoring and adjusting pH levels, water treatment operators can optimize the coagulation process, improve water quality, ensure regulatory compliance, and promote cost-effective solutions. As water treatment technologies advance, the significance of understanding the intricate relationship between PAC and pH will only increase, solidifying PAC's position as an essential component in modern water purification strategies.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





