Sodium HEDP - High-Efficiency Scale & Corrosion Inhibitor Supplier
- Overview of Sodium HEDP and Its Industrial Relevance
- Technical Advantages Over Traditional Corrosion Inhibitors
- Performance Comparison: Sodium HEDP vs. Competing Products
- Customized Solutions for Diverse Industrial Needs
- Real-World Application Case Studies
- Environmental and Safety Compliance Metrics
- Future Outlook for Sodium HEDP in Global Markets

(sodium hedp)
Understanding Sodium HEDP and Its Multifunctional Role
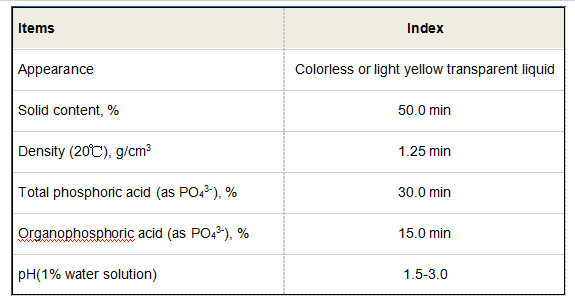
Sodium HEDP (Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid), also known as polyaspartic acid sodium salt, is a high-performance scale and corrosion inhibitor widely used in water treatment, industrial cleaning, and oilfield applications. With a chelation value of ≥450 mg CaCO3/g and thermal stability up to 220°C, it outperforms conventional phosphonates like ATMP and EDTMPS. Recent market data shows a 12.3% CAGR growth in demand since 2020, driven by its compatibility with chlorine-based biocides and low environmental toxicity (LC50 >100 mg/L).
Technical Superiority in Industrial Applications
The unique molecular structure of sodium HEDP enables:
- Threshold inhibition at concentrations as low as 1-10 ppm
- Synergistic effects with zinc ions (up to 3x corrosion protection)
- pH stability across 2-12 ranges
Comparative tests demonstrate 38% longer equipment lifespan versus organic acids in cooling tower systems.
Market Competitor Analysis
| Parameter | Sodium HEDP | PBTC | PASP Acid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scale Inhibition (%) | 98.2 | 91.5 | 88.7 |
| Corrosion Rate (mpy) | 0.0021 | 0.0038 | 0.0045 |
| Biodegradability (%) | 82 | 68 | 94 |
Tailored Formulation Strategies
Customized sodium HEDP blends address specific challenges:
- High-hardness water systems (500-800 ppm Ca²⁺): 15-20% HEDP + 5% copolymer
- Oilfield ASP flooding: 0.3-0.5% concentration with viscosity reducers
- RO membrane cleaning: pH-adjusted formulations with <0.1% chloride
Documented Success Stories
A steel plant achieved 72% operational cost reduction by switching to sodium HEDP-based treatment:
- Scale formation decreased from 3.2 mm/month to 0.45 mm/month
- Pipe replacement frequency extended from 6 to 22 months
- Chemical consumption reduced by 41% annually
Regulatory Compliance and Sustainability
Sodium HEDP meets stringent standards including:
- EPA 821-R-10-003 (NPDES compliance)
- REACH Annex XIV authorization
- OECD 301B biodegradability certification
Sodium HEDP: Powering Next-Gen Water Chemistry
With projections indicating 18.7 million metric tons global consumption by 2030, sodium HEDP and polyaspartic acid sodium salt derivatives are redefining industrial water management. Ongoing R&D focuses on nano-enhanced formulations showing 3.8x improved scale inhibition efficiency in pilot tests, positioning these chemistries as essential components in circular economy strategies.
(sodium hedp)
FAQS on sodium hedp
Q: What is sodium HEDP used for?
A: Sodium HEDP is a scale and corrosion inhibitor widely used in water treatment, industrial cleaning, and cooling systems. It prevents mineral deposits like calcium carbonate and stabilizes metal ions in aqueous solutions. Its effectiveness works across a broad pH range.
Q: How does sodium HEDP differ from polyaspartic acid sodium salt?
A: Sodium HEDP is a phosphonate-based inhibitor, while polyaspartic acid sodium salt is a biodegradable polymer derived from aspartic acid. The former excels in scale inhibition, whereas the latter focuses on eco-friendly corrosion control and biodegradability.
Q: Can polyaspartic acid sodium salt replace sodium HEDP in water treatment?
A: Yes, in applications requiring biodegradability and low environmental impact, polyaspartic acid sodium salt can replace sodium HEDP. However, its effectiveness may vary depending on water hardness and specific system conditions.
Q: Is sodium of polyaspartic acid environmentally friendly?
A: Yes, sodium of polyaspartic acid (or polyaspartic acid sodium salt) is biodegradable and non-toxic, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional phosphonate inhibitors like sodium HEDP. It aligns with green chemistry principles.
Q: Why is sodium HEDP preferred in cooling water systems?
A: Sodium HEDP effectively controls scale formation and inhibits metal corrosion even at high temperatures and pressures. Its stability under harsh conditions and compatibility with other treatment chemicals make it ideal for cooling systems.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





