scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals
The Role of Scale and Corrosion Inhibitor Chemicals in Industrial Processes
In industrial settings, particularly within the realms of water treatment and energy production, preventing scale formation and corrosion is crucial for maintaining system efficiency and longevity. Scale refers to mineral deposits that accumulate on the surfaces of equipment, while corrosion involves the gradual degradation of materials due to chemical reactions with their environment. Both phenomena can lead to significant operational issues, making the application of scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals essential.
Understanding Scale Formation and Corrosion
Scale formation typically occurs in systems that involve water—especially hard water, which contains high levels of calcium, magnesium, and other minerals. When water is heated or evaporated, these dissolved minerals can crystallize and adhere to surfaces, creating a layer of scale. This buildup can reduce heat transfer efficiency, increase energy consumption, and cause blockages in pipes and equipment.
Corrosion, on the other hand, is predominantly driven by the chemical composition of the water and environmental conditions, including temperature, pH, and oxygen levels. Corrosive agents can include dissolved oxygen, acids, and other electrolytes, which facilitate the electrochemical reactions leading to material degradation. This process can weaken structural integrity, leading to leaks, equipment failures, and costly downtimes.
The Importance of Inhibitors
Scale and corrosion inhibitors play a vital role in mitigating these issues. These chemicals work by altering the properties of the scale-forming minerals or by forming protective barriers on metal surfaces. Their use minimizes maintenance costs, extends the lifespan of equipment, and enhances overall system efficiency.
1. Types of Inhibitor Chemicals
Inhibitors can be broadly classified into two categories scale inhibitors and corrosion inhibitors
.- Scale Inhibitors These chemicals, such as polyphosphates, phosphonates, and organic acids, prevent the crystallization of scale-forming minerals. They do this by interfering with the nucleation and growth of crystals, making it easier for them to remain in a dissolved state.
scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals
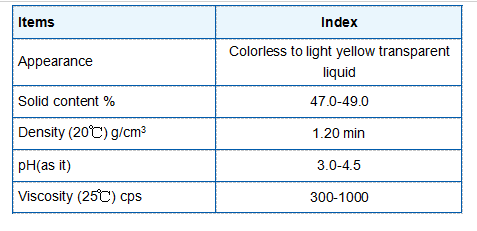
- Corrosion Inhibitors Commonly used corrosion inhibitors include azoles, glycine, and nitrite-based compounds. These substances either passivate the metal surface by forming a protective oxide layer or neutralize corrosive agents in the environment.
2. Mechanisms of Action
Scale inhibitors typically function by altering the solubility of minerals or modifying the surface characteristics of the materials being protected. They can modify the crystal growth process, creating less adherent and, therefore, easily removable deposits.
Corrosion inhibitors work through various mechanisms, including the formation of protective films, buffering of pH levels, and scavenging of dissolved oxygen. These actions help to reduce the rate of corrosion significantly, particularly in environments prone to aggressive chemical reactions.
Applications in Industry
Industries such as oil and gas, power generation, and water treatment rely heavily on scale and corrosion inhibitors. In oil and gas production, for instance, scale deposits can hinder flow and create dangerous pressure build-ups. Similarly, in power plants, scaling within boilers can lead to catastrophic failures if left unchecked.
The water treatment industry employs inhibitors to ensure that municipal and industrial water systems remain free from excessive scale and corrosion. This not only guarantees the efficient operation of water distribution systems but also protects municipal infrastructure and extends the life of treatment facilities.
Conclusion
The implementation of scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and equipment longevity across various industries. Their ability to mitigate the detrimental effects of scale and corrosion saves costs, reduces downtime, and ensures the reliability of essential industrial processes. As industrial challenges evolve, the development of more effective and environmentally friendly inhibitors will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in the sustainable management of resources.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





