Types of Flocculants Utilized in Water Treatment Processes and Their Effectiveness
Flocculants Used in Water Treatment An Overview
Water treatment is an essential process aimed at ensuring that water is safe for human consumption and ecological balance. One of the critical methods employed in this domain is flocculation, which plays a significant role in the removal of suspended solids and contaminants from water. Flocculants, the agents used in this process, facilitate the aggregation of particles, making them easier to settle or be removed through filtration.
Understanding Flocculation
Flocculation is a softening process in which fine particulates are agglomerated into a floc. This process often follows coagulation, where coagulants are added to destabilize the colloidal particles in water. Coagulation typically involves chemical reactions that promote the formation of larger aggregates. Once the particles are agglomerated into flocs, they can be separated from the water through sedimentation or filtration. Flocculants can be categorized into natural, synthetic, and semi-synthetic types, each with its specific applications and characteristics.
Types of Flocculants
1. Natural Flocculants These are derived from natural sources and include materials like starch, chitosan, and guar gum. Natural flocculants are biodegradable and are often preferred in applications where environmental impact is a significant concern. For example, chitosan, sourced from crustacean shells, is a popular choice in wastewater treatment due to its eco-friendliness and effectiveness in removing organic pollutants.
2. Synthetic Flocculants These are man-made polymers, which include types such as polyacrylamide (PAM), polyaluminum chloride (PAC), and others. Synthetic flocculants often provide a higher efficiency in reducing turbidity and have a tailored molecular structure that can be modified to suit specific water treatment needs. Polyacrylamide, for instance, is widely used in sludge dewatering processes and has proven to be effective in various industrial applications.
3. Semi-synthetic Flocculants These are modified natural substances that offer enhanced performance compared to their natural counterparts. They combine the benefits of natural flocculants with the enhanced efficiency of synthetic options. Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) exemplifies this category and is employed for its good interactive capabilities with charged particles in water.
The Role of Flocculants in Water Treatment
The application of flocculants in water treatment is multi-faceted. Their primary role is to reduce the turbidity of water bodies, making it suitable for consumption and environmental restoration. Flocculants help in
flocculants used in water treatment
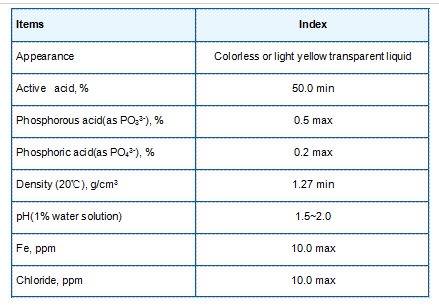
- Removing Suspended Solids Flocculants facilitate the aggregation of suspended particles, which include sediments, microorganisms, and organic matter, making it easier to remove them from water.
- Enhancing Sedimentation In treatment plants, flocculants enable faster sedimentation of flocs, which can significantly reduce the time required for the treatment process
.- Improving Filtration The presence of flocs enhances the efficiency of filtration systems, allowing for smaller particles to be captured more effectively, thus improving the quality of treated water.
- Supporting Wastewater Treatment In municipal and industrial wastewater treatment facilities, flocculants are essential for managing the dewatering of sludge, allowing for better handling and disposal of solid waste.
Environmental Considerations
While flocculants are effective in water treatment, it is crucial to consider their environmental impact. Some synthetic flocculants, particularly those based on polyacrylamides, can be toxic to aquatic life if released in high concentrations. Therefore, regulations and guidelines must be adhered to ensure that their usage does not harm the ecosystem.
Moreover, the growing demand for sustainable practices has led to increased interest in natural and biodegradable alternatives. Research is ongoing into developing more effective and environmentally friendly flocculants, assessing their efficacy in various water conditions.
Conclusion
Flocculants are an indispensable component of modern water treatment processes. By facilitating the removal of impurities, they contribute significantly to ensuring potable water is available and that wastewater is treated effectively. As technology progresses and environmental considerations become more critical, the evolution of flocculants will likely shape the future of water treatment practices, promoting both efficiency and sustainability. The continual exploration of natural and biodegradable alternatives presents exciting opportunities in this essential field, aiming for a cleaner and safer water supply for all.
-
Premium Isothiazolinones | Broad-Spectrum Biocidal SolutionsNewsAug.28,2025
-
LK-319 Special Scale And Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Plants: Advanced Solutions for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: Essential Chemical Solutions for Purification ProcessesNewsAug.22,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: Versatile Microbial Control Agents for Industrial and Consumer ApplicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor: Key Solutions for Water System Scale PreventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
Organophosphonates: Versatile Scale Inhibitors for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025





