Лип . 10, 2024 20:55
Back to list
Similar Phosphate Ester of Polyhydric Alcohol Understanding its Properties and Applications
Polyhydric alcohol phosphate esters are a group of compounds that have shown significant potential in various industrial applications. These compounds are frequently utilized as emulsifiers, surfactants, and lubricants due to their unique chemical structure and properties.
One of the key characteristics of polyhydric alcohol phosphate esters is their ability to act as emulsifiers. This means that they can help to mix together substances that would otherwise not be able to dissolve in each other, such as oil and water. This property makes them extremely valuable in the production of a wide range of products, from cosmetics and pharmaceuticals to food and beverages.
In addition to their emulsifying properties, polyhydric alcohol phosphate esters also act as surfactants. Surfactants are substances that help to reduce the surface tension between liquids, allowing them to mix more easily. This makes polyhydric alcohol phosphate esters ideal for use in cleaning products, where they can help to break down grease and dirt, making it easier to remove them from surfaces
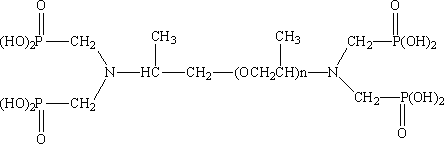
polyhydric alcohol phosphate ester. Furthermore, polyhydric alcohol phosphate esters are used as lubricants in a variety of industrial processes. Their ability to reduce friction between surfaces makes them indispensable in machinery and equipment, where they can help to improve efficiency and prolong the lifespan of moving parts. Overall, polyhydric alcohol phosphate esters are a versatile group of compounds that play a crucial role in numerous industries. Their emulsifying, surfactant, and lubricating properties make them essential in the production of a wide range of products, from cosmetics and pharmaceuticals to cleaning products and industrial machinery. In conclusion, polyhydric alcohol phosphate esters are an important class of compounds with a wide range of industrial applications. Their unique chemical structure and properties make them invaluable in industries such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, cleaning products, and machinery. As our understanding of these compounds continues to grow, so too will their potential for new and innovative applications.

polyhydric alcohol phosphate ester. Furthermore, polyhydric alcohol phosphate esters are used as lubricants in a variety of industrial processes. Their ability to reduce friction between surfaces makes them indispensable in machinery and equipment, where they can help to improve efficiency and prolong the lifespan of moving parts. Overall, polyhydric alcohol phosphate esters are a versatile group of compounds that play a crucial role in numerous industries. Their emulsifying, surfactant, and lubricating properties make them essential in the production of a wide range of products, from cosmetics and pharmaceuticals to cleaning products and industrial machinery. In conclusion, polyhydric alcohol phosphate esters are an important class of compounds with a wide range of industrial applications. Their unique chemical structure and properties make them invaluable in industries such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, cleaning products, and machinery. As our understanding of these compounds continues to grow, so too will their potential for new and innovative applications.
Share
Latest news
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





