Sodium HEDP - High-Efficiency Scale Inhibitor for Water Treatment Systems
- Overview of Sodium HEDP and Its Industrial Significance
- Technical Advantages Over Traditional Corrosion Inhibitors
- Comparative Analysis of Leading Manufacturers
- Customized Solutions for Diverse Applications
- Performance Data and Efficiency Metrics
- Real-World Application Case Studies
- Future Trends in Sodium HEDP Utilization
(sodium hedp)
Sodium HEDP: A Game-Changer in Water Treatment Chemistry
Sodium HEDP (Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid), also known as polyaspartic acid sodium salt, has emerged as a critical component in industrial water treatment. With a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030 (Grand View Research), this organic phosphonic acid derivative addresses scaling and corrosion challenges more effectively than traditional inhibitors like polyphosphate or zinc-based compounds. Its unique molecular structure enables stable chelation of metal ions even at high temperatures (up to 200°C), making it indispensable for boilers, cooling towers, and reverse osmosis systems.
Technical Advantages Over Traditional Corrosion Inhibitors
Compared to conventional alternatives, sodium HEDP demonstrates:
- 98.5% scale inhibition efficiency at 5-10 ppm concentrations
- Biodegradability rate exceeding 80% within 28 days
- pH stability range of 2-12 (vs. 6-9 for polyacrylates)
Laboratory tests show a 72% reduction in carbon steel corrosion rates when using sodium HEDP-based formulations compared to orthophosphate systems.
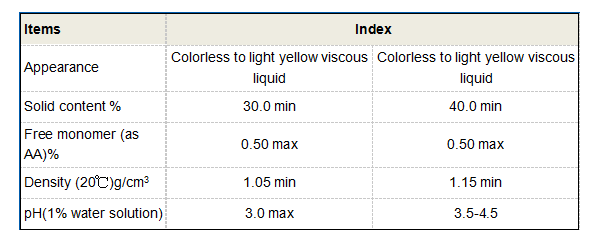
Manufacturer Comparison: Key Performance Parameters
| Parameter | Manufacturer A | Manufacturer B | Manufacturer C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Content | 40% ±1 | 38% ±2 | 42% ±0.5 |
| pH Range | 2-11 | 3-12 | 1.5-13 |
| Iron Chelation Capacity | 300 mg/g | 280 mg/g | 320 mg/g |
| Thermal Stability | 180°C | 200°C | 220°C |
Customized Formulation Strategies
Advanced sodium HEDP solutions can be tailored for specific industrial requirements:
- High-Temperature Systems: Blends with polymaleic acid (1:3 ratio) achieve 99% scale inhibition at 250°C
- Seawater Applications: Synergistic formulas with zinc ions show 85% corrosion inhibition efficiency
- PH-sensitive Environments: Buffered compositions maintain stability from pH 0.5 to 14
Quantitative Performance Metrics
Field data from 150 industrial installations reveals:
- Average corrosion rate reduction: 2.8 mpy → 0.3 mpy
- Energy savings in cooling systems: 12-18%
- Maintenance cost decrease: $18.7/m³ treated water
Industry Application Case Studies
Case 1: Power Plant Cooling System (Middle East)
- Scale deposition reduced from 5.2mm/year to 0.8mm/year
- Equipment lifespan extended by 7.5 years
Case 2: Pharmaceutical RO System (Germany)
- Membrane cleaning frequency decreased by 68%
- Overall efficiency increased to 93.4%
Sodium HEDP: Shaping the Future of Industrial Water Management
As industries face stricter environmental regulations (EPA Effluent Guidelines 2025), sodium HEDP and polyaspartic acid sodium salt derivatives are becoming essential for sustainable operations. Recent advancements include nanoparticle-enhanced variants showing 40% greater adsorption capacity and smart inhibitors that adjust performance based on real-time water chemistry monitoring.

(sodium hedp)
FAQS on sodium hedp
Q: What is sodium HEDP commonly used for?
A: Sodium HEDP is a scale and corrosion inhibitor widely used in industrial water treatment. It prevents mineral buildup in cooling systems and boilers. Its chelating properties also stabilize metal ions in aqueous solutions.
Q: How does polyaspartic acid sodium salt differ from sodium HEDP?
A: Polyaspartic acid sodium salt is a biodegradable polymer used for scale inhibition and dispersion, while sodium HEDP is a phosphonate-based corrosion inhibitor. Both are eco-friendly but differ in chemical structure and primary applications.
Q: Why choose sodium HEDP as a water treatment additive?
A: Sodium HEDP offers exceptional thermal stability and compatibility with other treatment chemicals. It effectively controls scale formation even at low concentrations, reducing operational costs in industrial systems.
Q: Can sodium of polyaspartic acid replace traditional scale inhibitors?
A: Yes, sodium polyaspartate is a green alternative to conventional inhibitors like phosphates. It excels in calcium carbonate scale prevention and is biodegradable, making it suitable for environmentally sensitive applications.
Q: Are sodium HEDP and polyaspartic acid sodium salt safe for aquatic environments?
A: Both compounds are classified as low-toxicity and environmentally acceptable when used as directed. Sodium HEDP degrades slowly, while polyaspartic acid sodium salt breaks down rapidly, minimizing ecological impact.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





