polyacrylamide production
Understanding Polyacrylamide Production A Comprehensive Overview
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a synthetic polymer that plays a crucial role in various industries due to its exceptional properties. This versatile compound is primarily produced through the polymerization of acrylamide monomers. Due to its ability to absorb water, enhance texture, and facilitate separation processes, polyacrylamide has found applications in fields such as water treatment, agriculture, and cosmetics. This article explores the process of polyacrylamide production and its implications in different sectors.
The Production Process
The production of polyacrylamide typically begins with the polymerization of acrylamide, a colorless crystalline solid. This process can be initiated through several methods, including thermal, redox, or photoinitiation. Among these, the most common method involves a free radical polymerization process, which can occur in either aqueous or organic solvents.
1. Raw Material Preparation The primary raw material, acrylamide, is synthesized from propylene, a byproduct of petroleum refining. Through a series of chemical reactions, propylene is converted into propylene oxide and then into acrylamide. The purity of acrylamide is crucial for the quality of the final polymer; thus, the raw material undergoes rigorous purification.
2. Initiation of Polymerization Once the acrylamide is prepared, the polymerization process begins. Free radical initiators, such as potassium persulfate, are added to the acrylamide solution. These initiators break down to generate free radicals, which then react with acrylamide monomers to form a growing polymer chain.
3. Polymerization Control Controlling the conditions under which polymerization occurs is vital. Factors such as temperature, pH, and concentration of the initiator are carefully managed to produce polyacrylamide of desired molecular weight and properties. The reaction can be performed in batch or continuous processes, depending on production needs.
4. Recovery and Purification After polymerization, the resulting polyacrylamide solution is treated to remove unreacted monomers and initiators. This step often employs processes like precipitation or dialysis. The purified polyacrylamide can then be concentrated, frozen, or dried into powder form for storage and transportation.
Applications of Polyacrylamide
polyacrylamide production
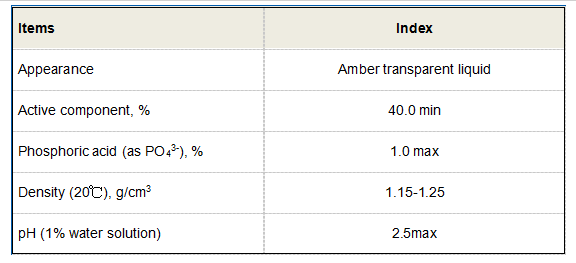
The unique characteristics of polyacrylamide, such as its ability to absorb water and form gels, long-chain structure, and ease of modification, have led to its diverse applications across various industries.
1. Water Treatment One of the most significant applications of polyacrylamide is in water treatment. It acts as a flocculant, helping to aggregate suspended solids and facilitate their removal in purification processes. Municipalities and industries utilize PAM for wastewater treatment to enhance the efficiency of sedimentation and filtration.
2. Agriculture In agriculture, polyacrylamide is used to improve soil structure and reduce erosion. When applied to soil, it enhances water retention, allowing for more efficient irrigation practices. Moreover, PAM can help transport fertilizers and nutrients to plants, ultimately increasing agricultural productivity.
3. Cosmetic and Personal Care Polyacrylamide is also employed in cosmetic formulations as a thickening agent and stabilizer. Its film-forming properties make it an attractive ingredient in products such as lotions, shampoos, and gels, providing a desirable texture and performance.
4. Industrial Processes In a range of industrial applications, polyacrylamide serves as a viscosity modifier, enhancing the performance of various liquids. Its role in enhanced oil recovery processes is notable, as it helps in the mobilization of crude oil, thereby improving extraction efficiency.
Environmental Considerations
While polyacrylamide offers numerous advantages, its production and use raise environmental concerns, particularly regarding the potential toxicity of unpolymerized acrylamide. Manufacturers must adhere to stringent regulations to mitigate risks associated with spills and exposure. Additionally, the biodegradability of polyacrylamide is a point of interest, as researchers are continuously exploring more sustainable alternatives or modifications to enhance its environmental profile.
Conclusion
Polyacrylamide production is a complex process that yields a valuable product with extensive applications across various sectors. Its benefits in water treatment, agriculture, cosmetics, and industrial processes reflect its versatility and importance in modern society. As industries strive for sustainability, understanding and improving the production and use of polyacrylamide will be essential for maximizing its benefits while minimizing environmental impacts.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





