amphoteric polyacrylamide
The Versatility of Amphoteric Polyacrylamide in Modern Applications
Amphoteric polyacrylamide (APAM) is a remarkable polymer that has garnered significant attention in various industrial and scientific fields due to its unique properties and versatile applications. As a copolymer of acrylic acid and acrylamide, APAM exhibits both anionic and cationic characteristics, making it an amphoteric substance. This duality in charge allows it to interact with a wide range of molecules, providing unique functionality that is advantageous in various applications.
Understanding Amphoteric Properties
The term 'amphoteric' refers to a substance that can act as both an acid and a base depending on the surrounding environment. In the case of amphoteric polyacrylamide, its structure contains both positive and negative ionic groups that can respond differently to changes in pH and ionic strength. This flexibility enables APAM to form stable complexes with different substances, which makes it suitable for a wide range of uses, particularly in environmental and industrial applications.
Water Treatment Applications
One of the most significant applications of amphoteric polyacrylamide is in water treatment. The ability of APAM to flocculate and separate suspended particles from water is invaluable. In many water treatment processes, APAM is used as a flocculant to enhance sedimentation and clarification of wastewater. The anionic character of the polymer allows it to bind with positively charged particles, while the cationic portions can attract negatively charged contaminants. This dual capability significantly improves the efficiency of the flocculation process, leading to cleaner water and reduced chemical usage.
Enhanced Oil Recovery
amphoteric polyacrylamide
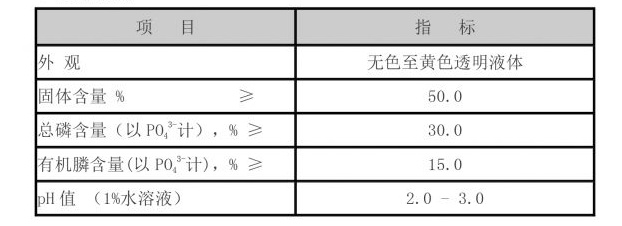
In the oil and gas industry, APAM plays a critical role in enhanced oil recovery (EOR). The polymer's properties allow it to improve the mobility of oil within reservoirs, making it easier to extract. APAM can modify the viscosity of water flooding processes by thickening the water, which increases the efficiency of oil displacement. This results in higher recovery rates compared to traditional methods. The amphoteric nature of APAM allows it to interact with different types of crude oil and water, making it a highly effective tool in EOR strategies.
Agricultural Applications
Amphoteric polyacrylamide is also making waves in agriculture, particularly in soil conditioning and erosion control. By forming a protective film around soil particles, APAM helps to retain moisture, improve soil structure, and reduce erosion caused by wind and water. Its ability to bind with both negatively and positively charged soil particles enhances the soil's nutrient-holding capacity, leading to improved crop yields. Furthermore, APAM's biodegradable properties make it an environmentally friendly option for sustainable agricultural practices.
Biomedical Applications
The versatility of amphoteric polyacrylamide extends to the biomedical field as well. Its biocompatibility and ability to form hydrogels have made it an essential material in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering. APAM-based hydrogels can encapsulate therapeutic agents and release them in a controlled manner, enhancing their effectiveness and reducing side effects. Additionally, researchers are exploring its use in wound dressings and as scaffolds for cell growth, highlighting its potential to revolutionize medical treatments.
Conclusion
Amphoteric polyacrylamide represents a fascinating intersection of chemistry and practical application. Its unique properties and versatility enable it to address critical challenges in various industries, including water treatment, oil recovery, agriculture, and medicine. As research continues to uncover new potential applications and improve existing processes, APAM is poised to play an increasingly vital role in innovative solutions for modern problems. The marriage of its amphoteric nature with technological advancements promises an exciting future for this polymer, ensuring its relevance across multiple sectors. As industries strive for efficiency and sustainability, amphoteric polyacrylamide stands out as a key player in the development of advanced materials and processes that benefit society and the environment alike.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





