polyaluminum chloride coagulant
Polyaluminum Chloride Coagulant A Key Component in Water Treatment
Polyaluminum chloride (PAC) is an inorganic polymer that has gained significant attention for its effectiveness as a coagulant in water treatment processes. It is mainly used for purifying drinking water and treating wastewater due to its ability to remove suspended solids, organic matter, and various impurities from water. The coagulation process involves the aggregation of fine particles into larger clusters, which can then be easily separated from water.
One of the major advantages of PAC over traditional coagulants like aluminum sulfate is its higher efficiency at a lower dosage. This results in reduced sludge production, thereby lowering the costs associated with disposal. PAC operates effectively across a wide range of pH levels, making it adaptable to various water quality conditions. Its performance is particularly notable in treating turbid waters, where it can significantly enhance sedimentation rates.
During the coagulation process, PAC hydrolyzes in water to form aluminum hydroxide, which acts as a bridge to connect particles together. The resulting floc aggregates are larger and heavier, allowing them to settle more quickly during the sedimentation phase. This efficient separation process is crucial for both drinking water production and wastewater management, ensuring that the treated water meets the required quality standards.
polyaluminum chloride coagulant
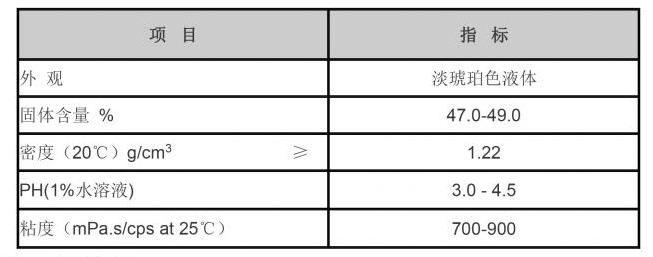
In addition to its effectiveness in coagulation, PAC is known for its low toxicity and environmental friendliness. Unlike some other chemical coagulants, PAC does not introduce harmful residuals into the water, making it a safer choice for both operators and consumers. Its formulation is also less impacted by temperature changes, which means it can perform well in various climatic conditions.
The production of PAC typically involves reacting aluminum hydroxide with hydrochloric acid, resulting in a product that is available in both liquid and solid forms
. Its versatility allows for easy application in different types of treatment facilities, from large municipal water treatment plants to smaller decentralized systems.In conclusion, polyaluminum chloride coagulant plays a vital role in the realm of water treatment. Its superior coagulation properties, combined with environmental safety and cost-efficiency, make it an increasingly popular choice for a wide range of applications. As water quality continues to be a pressing global issue, the use of PAC is expected to grow, further contributing to the provision of safe and clean water for communities worldwide.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





