Polyacrylamide Production
Polyacrylamide Production An Overview
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a versatile polymer widely used in various industries, including water treatment, agriculture, mining, and oil recovery
. Its significance stems from its unique properties, such as high molecular weight and excellent water-absorbing capabilities, which enable it to enhance several industrial processes. This article aims to provide an overview of polyacrylamide production, its methods, and its applications.The production of polyacrylamide typically involves the polymerization of acrylamide, a water-soluble monomer. There are two primary methods for the synthesis of polyacrylamide batch polymerization and continuous polymerization. In the batch polymerization process, acrylamide monomers are mixed with water and a polymerization initiator. The mixture is heated to facilitate the reaction, which results in the formation of polyacrylamide. This method is commonly used for producing small batches of the polymer and allows for greater control over reaction conditions.
On the other hand, continuous polymerization offers a more efficient approach for large-scale production. In this method, acrylamide is continuously fed into a reactor along with an initiator and water. The reaction occurs in a controlled environment, allowing for continuous removal of the heat generated during polymerization. This process tends to produce polyacrylamide with consistent properties and is suitable for large volumes, making it ideal for industrial applications.
polyacrylamide production
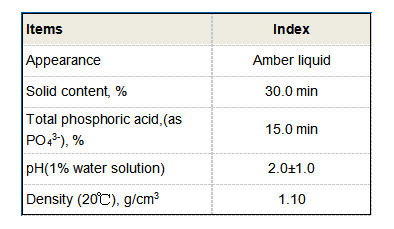
The choice of polymerization method can significantly influence the molecular weight and characteristics of the final polyacrylamide product. Higher molecular weight polyacrylamides tend to offer better performance in applications such as flocculation and thickening, while lower molecular weight variants may be preferred in certain scenarios like soil conditioner applications.
Once produced, polyacrylamide can be modified to enhance its properties or tailor it for specific applications. For instance, it can be cross-linked to create hydrogels or blended with other polymers to improve its functionality. The resulting products can be classified into anionic, cationic, and non-ionic polyacrylamides, each serving distinct roles in various processes.
The applications of polyacrylamide are broad and impactful. In water treatment, it acts as a flocculant, aiding in the removal of suspended particles from wastewater, thereby improving water quality. In agriculture, PAM is often used as a soil conditioner, helping to reduce erosion and improve water retention in soils. Furthermore, in the mining and oil industries, polyacrylamide is critical for enhancing extraction processes, improving yield, and supporting efficient resource management.
In summary, polyacrylamide production is a crucial process that leads to the creation of a polymer with wide-ranging applications across multiple industries. As the demand for more effective and environmentally friendly solutions increases, ongoing research and development in polyacrylamide production techniques are likely to yield innovative products that meet the needs of the future. With its exceptional properties and adaptability, polyacrylamide is poised to remain a key player in various industrial applications.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





