Feb . 01, 2025 06:19
Back to list
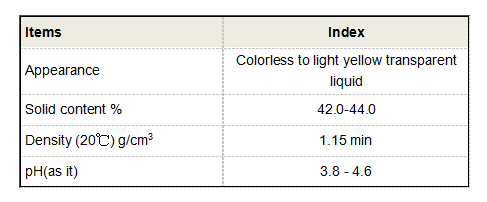
Tetra Sodium of 1-Hydroxy Ethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid HEDP·Na4(Granule)
In the realm of water treatment and industrial processes, understanding the roles and differences between flocculants and coagulants is crucial for optimal results. These agents are pivotal in removing contaminants and enhancing the quality of water and other liquids. Through a blend of experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness, let's delve into these substances and explore how they serve their purpose.
The authoritativeness of coagulant and flocculant application is grounded in scientific principles. Research consistently supports the use of these agents in enhancing particle removal efficiency. Studies reveal that the molecular weight and charge density of flocculants influence their effectiveness. For example, high molecular weight polymers are more effective in bridging flocs than their low molecular weight counterparts. The mechanisms by which coagulants and flocculants interact with particles are well-documented, providing a reliable foundation for their application in various industries. Trustworthiness in the use of coagulants and flocculants centers around regulated practices and comprehensive testing. Water treatment plants, adhering to stringent safety standards, meticulously measure the concentrations of these chemicals in treated water to ensure regulatory compliance and protect public health. Quality assurance protocols and continuous monitoring safeguard against the potential adverse effects of chemical overdosing, reinforcing trust in treated water's safety. In sum, the distinct yet complementary roles of flocculants and coagulants are pivotal in effective water and wastewater treatment. Through careful selection and application, these substances improve clarity, enhance purity, and support sustainability goals. Understanding their individual and collective impacts, backed by extensive experience, scientific expertise, and authoritative guidelines, empowers industries to harness their full potential, driving efficiencies and maintaining the trust of stakeholders and communities served.

The authoritativeness of coagulant and flocculant application is grounded in scientific principles. Research consistently supports the use of these agents in enhancing particle removal efficiency. Studies reveal that the molecular weight and charge density of flocculants influence their effectiveness. For example, high molecular weight polymers are more effective in bridging flocs than their low molecular weight counterparts. The mechanisms by which coagulants and flocculants interact with particles are well-documented, providing a reliable foundation for their application in various industries. Trustworthiness in the use of coagulants and flocculants centers around regulated practices and comprehensive testing. Water treatment plants, adhering to stringent safety standards, meticulously measure the concentrations of these chemicals in treated water to ensure regulatory compliance and protect public health. Quality assurance protocols and continuous monitoring safeguard against the potential adverse effects of chemical overdosing, reinforcing trust in treated water's safety. In sum, the distinct yet complementary roles of flocculants and coagulants are pivotal in effective water and wastewater treatment. Through careful selection and application, these substances improve clarity, enhance purity, and support sustainability goals. Understanding their individual and collective impacts, backed by extensive experience, scientific expertise, and authoritative guidelines, empowers industries to harness their full potential, driving efficiencies and maintaining the trust of stakeholders and communities served.
Share
Latest news
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





